IntS6 and the Integrator phosphatase module tune the efficiency of select premature transcription termination events
- PMID: 37995689
- PMCID: PMC10841813
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.10.035
IntS6 and the Integrator phosphatase module tune the efficiency of select premature transcription termination events
Abstract
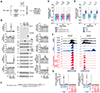
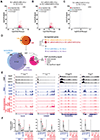
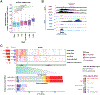
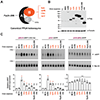
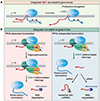
The metazoan-specific Integrator complex catalyzes 3' end processing of small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) and premature termination that attenuates the transcription of many protein-coding genes. Integrator has RNA endonuclease and protein phosphatase activities, but it remains unclear if both are required for complex function. Here, we show IntS6 (Integrator subunit 6) over-expression blocks Integrator function at a subset of Drosophila protein-coding genes, although having no effect on snRNAs or attenuation of other loci. Over-expressed IntS6 titrates protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) subunits, thereby only affecting gene loci where phosphatase activity is necessary for Integrator function. IntS6 functions analogous to a PP2A regulatory B subunit as over-expression of canonical B subunits, which do not bind Integrator, is also sufficient to inhibit Integrator activity. These results show that the phosphatase module is critical at only a subset of Integrator-regulated genes and point to PP2A recruitment as a tunable step that modulates transcription termination efficiency.
Keywords: 3′ end processing; INTAC; Integrator complex; Integrator subunit 6; PP2A; RNA polymerase II; promoter-proximal termination; protein phosphatase 2A; snRNA; transcription.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests J.E.W. serves as a consultant for Laronde.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

