The extrafollicular B cell response is a hallmark of childhood idiopathic nephrotic syndrome
- PMID: 37996443
- PMCID: PMC10667257
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-43504-8
The extrafollicular B cell response is a hallmark of childhood idiopathic nephrotic syndrome
Abstract
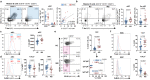
The efficacy of the B cell-targeting drug rituximab (RTX) in childhood idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (INS) suggests that B cells may be implicated in disease pathogenesis. However, B cell characterization in children with INS remains limited. Here, using single-cell RNA sequencing, we demonstrate that a B cell transcriptional program poised for effector functions represents the major immune perturbation in blood samples from children with active INS. This transcriptional profile was associated with an extrafollicular B cell response marked by the expansion of atypical B cells (atBCs), marginal zone-like B cells, and antibody-secreting cells (ASCs). Flow cytometry of blood from 13 children with active INS and 24 healthy donors confirmed the presence of an extrafollicular B cell response denoted by the expansion of proliferating RTX-sensitive extrafollicular (CXCR5-) CD21low T-bet+ CD11c+ atBCs and short-lived T-bet+ ASCs in INS. Together, our study provides evidence for an extrafollicular origin for humoral immunity in active INS.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Noone DG, Iijima K, Parekh R. Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in children. Lancet. 2018;392:61–74. - PubMed
-
- Eddy AA, Symons JM. Nephrotic syndrome in childhood. Lancet. 2003;362:629–639. - PubMed
-
- Liu, J. & Guan, F. B cell phenotype, activity, and function in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr. Res.10.1038/s41390-022-02336-w (2022). - PubMed
-
- Takei T, et al. Effect of single-dose rituximab on steroid-dependent minimal-change nephrotic syndrome in adults. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2013;28:1225–1232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- PJT-166006/Gouvernement du Canada | Canadian Institutes of Health Research (Instituts de Recherche en Santé du Canada)
- PJT-166006/Gouvernement du Canada | Canadian Institutes of Health Research (Instituts de Recherche en Santé du Canada)
- PJT-166006/Gouvernement du Canada | Canadian Institutes of Health Research (Instituts de Recherche en Santé du Canada)
- KHRG-190010/Kidney Foundation of Canada (La Fondation canadienne du rein)
- KHRG-190010/Kidney Foundation of Canada (La Fondation canadienne du rein)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

