Cytokine-armed dendritic cell progenitors for antigen-agnostic cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 37996514
- PMCID: PMC10899110
- DOI: 10.1038/s43018-023-00668-y
Cytokine-armed dendritic cell progenitors for antigen-agnostic cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
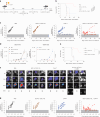
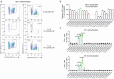
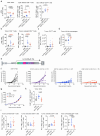
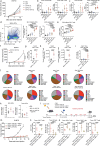
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting myeloid cells that regulate T cell activation, trafficking and function. Monocyte-derived DCs pulsed with tumor antigens have been tested extensively for therapeutic vaccination in cancer, with mixed clinical results. Here, we present a cell-therapy platform based on mouse or human DC progenitors (DCPs) engineered to produce two immunostimulatory cytokines, IL-12 and FLT3L. Cytokine-armed DCPs differentiated into conventional type-I DCs (cDC1) and suppressed tumor growth, including melanoma and autochthonous liver models, without the need for antigen loading or myeloablative host conditioning. Tumor response involved synergy between IL-12 and FLT3L and was associated with natural killer and T cell infiltration and activation, M1-like macrophage programming and ischemic tumor necrosis. Antitumor immunity was dependent on endogenous cDC1 expansion and interferon-γ signaling but did not require CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity. Cytokine-armed DCPs synergized effectively with anti-GD2 chimeric-antigen receptor (CAR) T cells in eradicating intracranial gliomas in mice, illustrating their potential in combination therapies.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
M.D.P. has received sponsored research grants from EVIR Therapeutics, Hoffmann La-Roche and Deciphera Pharmaceuticals, serves on the Scientific Advisory Boards of EVIR Therapeutics, Montis Biosciences, Macomics, Deciphera Pharmaceuticals, Light Chain Bioscience/Novimmune and Genenta, and is an inventor on patents on engineered DCs filed by EPFL. D.M. is a consultant for Limula and MPC Therapeutics, scientific co-founder of Cellula Therapeutics and is an inventor on patents related to CAR-T cell therapy filed by the University of Pennsylvania, Istituto Oncologico della Svizzera Italiana (IOSI) and the University of Geneva. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures













References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

