Anomalous peroxidase activity of cytochrome c is the primary pathogenic target in Barth syndrome
- PMID: 37996701
- PMCID: PMC11213643
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-023-00926-4
Anomalous peroxidase activity of cytochrome c is the primary pathogenic target in Barth syndrome
Abstract
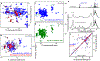
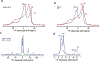
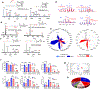
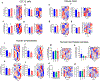
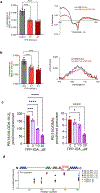
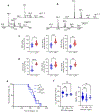
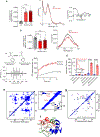
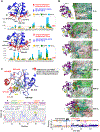
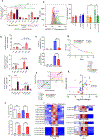
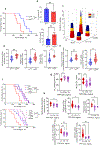
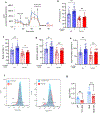
Barth syndrome (BTHS) is a life-threatening genetic disorder with unknown pathogenicity caused by mutations in TAFAZZIN (TAZ) that affect remodeling of mitochondrial cardiolipin (CL). TAZ deficiency leads to accumulation of mono-lyso-CL (MLCL), which forms a peroxidase complex with cytochrome c (cyt c) capable of oxidizing polyunsaturated fatty acid-containing lipids. We hypothesized that accumulation of MLCL facilitates formation of anomalous MLCL-cyt c peroxidase complexes and peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acid phospholipids as the primary BTHS pathogenic mechanism. Using genetic, biochemical/biophysical, redox lipidomic and computational approaches, we reveal mechanisms of peroxidase-competent MLCL-cyt c complexation and increased phospholipid peroxidation in different TAZ-deficient cells and animal models and in pre-transplant biopsies from hearts of patients with BTHS. A specific mitochondria-targeted anti-peroxidase agent inhibited MLCL-cyt c peroxidase activity, prevented phospholipid peroxidation, improved mitochondrial respiration of TAZ-deficient C2C12 myoblasts and restored exercise endurance in a BTHS Drosophila model. Targeting MLCL-cyt c peroxidase offers therapeutic approaches to BTHS treatment.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

