Impact of relaxing incisions on maxillofacial growth following Sommerlad-Furlow modified technique in patients with isolated cleft palate: a preliminary comparative study
- PMID: 37996863
- PMCID: PMC10668437
- DOI: 10.1186/s12893-023-02247-5
Impact of relaxing incisions on maxillofacial growth following Sommerlad-Furlow modified technique in patients with isolated cleft palate: a preliminary comparative study
Abstract
Objective: To estimate the impact of relaxing incisions on maxillofacial growth following Sommerlad-Furlow modified technique in patients with isolated cleft palate.
Study design: A Retrospective Cohort Study.
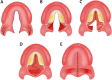
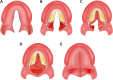
Methods: A total of 90 participants, 60 patients with non-syndromic isolated soft and hard cleft palate underwent primary palatoplasty (30 patients received the Sommerlad-Furlow modified technique without relaxing incision (S.F-RI group), and 30 received Sommerlad-Furlow modified technique with relaxing (S.F+RI group) with no significant difference found between them regarding the cleft type, cleft width, and age at repair. While the other 30 were healthy noncleft participants with skeletal class I pattern as a Control group. The control group (C group) was matched with the patient groups in number, age, and sex. All participants had lateral cephalometric radiographs at least 5 years old age. The lateral cephalometric radiographs were taken with the same equipment by the same experienced radiologist while the participants were in centric occlusion and a standardized upright position, with the transporionic axis and Frankfort horizontal plane parallel to the surface of the floor. A well-trained assessor (S. Elayah) used DOLPHIN Imaging Software to trace twice to eliminate measurement errors. All the study variables were measured using stable landmarks, including 12 linear and 10 angular variants.
Results: The mean age at collection of cephalograms was 6.03 ± 0.80 in the S.F+RI group, 5.96 ± 0.76 in the S.F-RI group, and 5.91 ± 0.87 in the C group. Regarding cranial base, the results showed no statistically significant differences between the three groups in S-N and S-N-Ba. While the S.F+R.I group had a significantly shortest S-Ba than the S.F-R.I & C groups (P = 0.01 & P < 0.01), but there was no statistically significant difference between S.F-R.I & C groups (P = 0.71). Regarding the skeletal maxilla, there was no significant difference between the S.F+R.I and S.F-R.I groups in all linear measurements (N-ANS and S-PM) except Co-A, the S.F+R.I group had significantly shorter Co-A than the S.F-R.I & C groups (P = < 0.01). While the angular measurement, S.F+R.I group had significantly less SNA angle than the S.F-R.I & C groups (P = < 0.01). Regarding mandibular bone, there were no statistically significant differences in all linear and angular mandibular measurements between the S.F+R.I and S.F-R.I.groups. Regarding intermaxillary relation, the S.F+R.I group had significant differences in Co-Gn-Co-A and ANB compared to the S.F-R.I & C groups (P = < 0.01). While there was no statistically significant difference in PP-MP between the three groups.
Conclusion: As a preliminary report, the Sommerlad-Furlow modified technique without relaxing incisions was found to have a good maxillary positioning in the face and a satisfactory intermaxillary relationship compared to the Sommerlad-Furlow modified technique with relaxing incisions.
Keywords: Cleft palate; Maxillofacial growth; Palatoplasty; Relaxing incisions.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

