Tomographic analysis of relationship of mandibular morphology and third molars eruption
- PMID: 37996868
- PMCID: PMC10668375
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-023-03653-0
Tomographic analysis of relationship of mandibular morphology and third molars eruption
Abstract
Background: Lower third molars (L3M) are the last teeth to erupt in the oral cavity. Uneruption of these teeth still raises questions about its causes, in the literature (1) genetic factors, (2) dental lamina activity and, mainly, (3) insufficient growth and development of the bone bases are included. While the lack of space theory influenced by mandibular morphology and size of L3M was argued to be the main reason for L3M impaction, there is a limitation in the literature in examining such association using more accurate tomographic analysis obtained from CBCT. This work aimed to evaluate the relationship between mandibular morphology and the eruption of L3M.
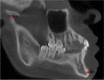
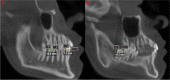
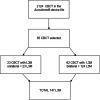
Methods: In this regard, 85 Cone Beam Computed Tomographies (CBCT), with 147 L3M, were selected from the archives of the Department of Surgery, Stomatology, Pathology and Radiology, Bauru School of Dentistry, obtained using an Accuitomo® Morita device and using the Dolphin Imaging 11.9 software. L3M eruption was related to linear measurements of jaw length (Co-Gn), retromolar space dimension (D2R), mesiodistal width of the L3M crowns, mandibular first molars (L1M) and mandibular canines (LC) and the angle mandibular (Ar-Go-Me). Independent samples t-test, chi-square tests and logistic regression were performed adopting a significance level of 5%.
Results: The average mandible length of 116.446 mm + 6.415 mm, retromolar space of 11.634 mm + 2.385 mm, mesiodistal size of the L3M of 10.054 mm + 0.941 mm, sum of the mesiodistal widths of the L1M and LC of 15.564 mm + 1.218 mm and mandibular angle of 127.23° + 6.109. There was no statistically significant association between these factors and the eruption.
Conclusion: With the results obtained in this study, we conclude that the length and angle of the mandible, teeth size and dimension of the retromolar space are not associated with the L3M eruption.
Keywords: Mandible; Third molar; Tomography; Tooth eruption.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Radiographic assessment of lower third molar eruption in different anteroposterior skeletal patterns and age-related groups.Angle Orthod. 2015 Jul;85(4):577-84. doi: 10.2319/062714-463.1. Epub 2014 Sep 22. Angle Orthod. 2015. PMID: 25244087 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of mandibular retromolar space in adults with regard to third molar eruption status.Clin Oral Investig. 2023 Feb;27(2):671-680. doi: 10.1007/s00784-022-04782-6. Epub 2022 Nov 14. Clin Oral Investig. 2023. PMID: 36374353
-
Comparison of the mandibular retromolar space in adults with different sagittal skeletal types and eruption patterns of the mandibular third-molar: a cone-beam computed tomography study.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Sep 19;24(1):1112. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04815-4. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39300426 Free PMC article.
-
Third-molar mineralization as a function of available retromolar space.Acta Odontol Scand. 2016 Oct;74(7):509-517. doi: 10.1080/00016357.2016.1209240. Epub 2016 Jul 22. Acta Odontol Scand. 2016. PMID: 27448555
-
Evaluation of root canal morphology of human primary molars by using CBCT and comprehensive review of the literature.Acta Odontol Scand. 2016;74(4):250-8. doi: 10.3109/00016357.2015.1104721. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Acta Odontol Scand. 2016. PMID: 26523502 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of extraction vs. non-extraction orthodontic treatment on the angulation of third molars on panoramic radiographs: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Prog Orthod. 2025 Jul 17;26(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s40510-025-00573-3. Prog Orthod. 2025. PMID: 40676470 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Muhsin H, Brizuela M. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Oral surgery, extraction of mandibular third molars. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

