Exploring the underlying mechanisms of fisetin in the treatment of hepatic insulin resistance via network pharmacology and in vitro validation
- PMID: 37996895
- PMCID: PMC10666360
- DOI: 10.1186/s12986-023-00770-z
Exploring the underlying mechanisms of fisetin in the treatment of hepatic insulin resistance via network pharmacology and in vitro validation
Abstract
Objective: To characterize potential mechanisms of fisetin on hepatic insulin resistance (IR) using network pharmacology and in vitro validation.
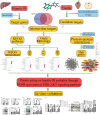
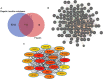
Methods: Putative targets of fisetin were retrieved from the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology database, whereas the potential genes of hepatic IR were obtained from GeneCards database. A protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed according to the intersection targets of fisetin and hepatic IR using the Venn diagram. The biological functions and potential pathways related to genes were determined using Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses. Cell experiments were also conducted to further verify the mechanism of fisetin on hepatic IR.
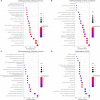
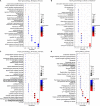
Results: A total of 118 potential targets from fisetin were associated with hepatic IR. The areas of nodes and corresponding degree values of TP53, AKT1, TNF, IL6, CASP3, CTNNB1, JUN, SRC, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), and HSP90AA1 were larger and could be easily found in the PPI network. Furthermore, GO analysis revealed that these key targets were significantly involved in multiple biological processes that participated in oxidative stress and serine/threonine kinase activity. KEGG enrichment analysis showed that the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway was a significant pathway involved in hepatic IR. Our in vitro results demonstrated that fisetin treatment increased the expressions of EGFR and IRS in HepG2 and L02 cells under normal or IR conditions. Western blot results revealed that p-AKT/AKT levels were significantly up-regulated, suggesting that fisetin was involved in the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to regulate insulin signaling.
Conclusion: We explored the pharmacological actions and the potential molecular mechanism of fisetin in treating hepatic IR from a holistic perspective. Our study lays a theoretical foundation for the development of fisetin for type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: Epidermal growth factor receptor; Fisetin; Hepatic insulin resistance; Network pharmacology; PI3K/AKT signaling.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Network pharmacology identifies fisetin as a treatment for osteoporosis that activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in BMSCs.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Apr 22;18(1):312. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03761-1. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 37087476 Free PMC article.
-
A network pharmacology approach and experimental validation to investigate the anticancer mechanism and potential active targets of ethanol extract of Wei-Tong-Xin against colorectal cancer through induction of apoptosis via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Mar 1;303:115933. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115933. Epub 2022 Nov 18. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36403742
-
Network pharmacology-based prediction and validation of the active ingredients and potential mechanisms of the Huangxiong formula for treating ischemic stroke.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Aug 10;312:116507. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116507. Epub 2023 Apr 18. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37080367
-
Potential Molecular Mechanisms of Ephedra Herb in the Treatment of Nephrotic Syndrome Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jul 5;2022:9214589. doi: 10.1155/2022/9214589. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35837376 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism of peach kernel and safflower herb-pair for the treatment of liver fibrosis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Apr 21;102(16):e33593. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033593. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37083803 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Optimized Effects of Fisetin and Hydroxychloroquine on ER Stress and Autophagy in Nonalcoholic Fatty Pancreas Disease in Mice.J Diabetes Res. 2025 Apr 14;2025:2795127. doi: 10.1155/jdr/2795127. eCollection 2025. J Diabetes Res. 2025. PMID: 40260275 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolites of traditional Chinese medicine targeting PI3K/AKT signaling pathway for hypoglycemic effect in type 2 diabetes.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 10;15:1373711. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1373711. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38799166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experimental cell models of insulin resistance: overview and appraisal.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Dec 19;15:1469565. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1469565. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39749015 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

