Chronological analysis of periodontal bone loss in experimental periodontitis in mice
- PMID: 37997536
- PMCID: PMC10728515
- DOI: 10.1002/cre2.806
Chronological analysis of periodontal bone loss in experimental periodontitis in mice
Abstract
Objectives: Periodontal disease is understood to be a result of dysbiotic interactions between the host and the biofilm, causing a unique reaction for each individual, which in turn characterizes their susceptibility. The objective of this study was to chronologically evaluate periodontal tissue destruction induced by systemic bacterial challenge in known susceptible (BALB/c) and resistant (C57BL/6) mouse lineages.
Material and methods: Animals, 6-8 weeks old, were allocated into three experimental groups: Negative control (C), Gavage with sterile carboxymethyl cellulose 2%-without bacteria (Sham), and Gavage with carboxymethyl cellulose 2% + Porphyromonas gingivalis (Pg-W83). Before infection, all animals received antibiotic treatment (sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim, 400/80 mg/5 mL) for 7 days, followed by 3 days of rest. Microbial challenge was performed 3 times per week for 1, 2, or 3 weeks. After that, the animals were kept until the completion of 42 days of experiments, when they were euthanized. The alveolar bone microarchitecture was assessed by computed microtomography.
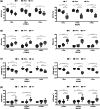
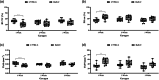
Results: Both C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice exhibited significant bone volume loss and lower trabecular thickness as well as greater bone porosity compared to the (C) and (Sham) groups after 1 week of microbial challenge (p < .001). When comparing only the gavage groups regarding disease implantation, time and lineage, it was possible to observe that within 1 week of induction the disease was more established in BALB/c than in C57BL/6 (p < .05).
Conclusions: Our results reflected that after 1 week of microbial challenge, there was evidence of alveolar bone loss for both lineages, with the loss observed in BALB/c mice being more pronounced.
Keywords: alveolar bone loss; host microbiota interactions; inflammation; periodontal diseases.
© 2023 The Authors. Clinical and Experimental Dental Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Abusleme, L. , Dupuy, A. K. , Dutzan, N. , Silva, N. , Burleson, J. A. , Strausbaugh, L. D. , Gamonal, J. , & Diaz, P. I. (2013). The subgingival microbiome in health and periodontitis and its relationship with community biomass and inflammation. The ISME Journal, 7(5), 1016–1025. 10.1038/ismej.2012.174 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baker, P. J. , Dixon, M. , Evans, R. T. , Dufour, L. , Johnson, E. , & Roopenian, D. C. (1999). CD4+ T cells and the proinflammatory cytokines gamma interferon and interleukin‐6 contribute to alveolar bone loss in mice. Infection and Immunity, 67(6), 2804–2809. 10.1128/iai.67.6.2804-2809.1999 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

