Soluble ST2 in Heart Failure: A Clinical Role beyond B-Type Natriuretic Peptide
- PMID: 37998526
- PMCID: PMC10672197
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd10110468
Soluble ST2 in Heart Failure: A Clinical Role beyond B-Type Natriuretic Peptide
Abstract
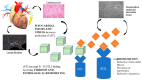
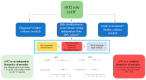
Soluble (s)ST2 has been proposed as a useful biomarker for heart failure (HF) patient management. Myocardial damage or mechanical stress stimulate sST2 release. ST2 competes with a membrane bound receptor (ST2 ligand, or ST2L) for interleukin-33 (IL-33) binding, inhibiting the effects induced by the ST2L/IL-33 interaction so that excessive sST2 may contribute to myocardial fibrosis and ventricular remodeling. Compared to natriuretic peptides (NPs), sST2 concentration is not substantially affected by age, sex, body mass index, kidney function, atrial fibrillation, anemia, or HF etiology, and has low intra-individual variation. Its prognostic role as an independent marker is well reported in the literature. However, there is a gap on its use in combination with NPs, currently the only biomarkers recommended by European and American guidelines for HF management. Reflecting the activation of two distinct biological systems, a benefit from the use of sST2 and NP in combination is advocated. The aim of this review is to report the current scientific knowledge on sST2 in the acute and chronic HF settings with a particular attention to its additive role to natriuretic peptides (NPs).
Keywords: heart failure; natriuretic peptides; solubleST2.
Conflict of interest statement
T.A.Z. reports research grants from the Austrian Science Funds and the German Research Foundation, honoraria for serving on advisory boards from Boehringer Ingelheim, personal fees from Alkem Lab. Ltd., AstraZeneca, Bayer AG, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, and educational grants from Eli Lilly and Company. R.M.I. has consulted for Daiichi-Sankyo, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim.
Figures
References
-
- Núñez J., de la Espriella R., Rossignol P., Voors A.A., Mullens W., Metra M., Chioncel O., Januzzi J.L., Mueller C., Richards A.M., et al. Congestion in heart failure: A circulating biomarker-based perspective. A review from the Biomarkers Working Group of the Heart Failure Association, European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2022;24:1751–1766. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.2664. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Authors/Task Force Members. McDonagh T.A., Metra M., Adamo M., Gardner R.S., Baumbach A., Böhm M., Burri H., Butler J., Čelutkienė J., et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: Developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2022;24:4–131. - PubMed
-
- Heidenreich P.A., Bozkurt B., Aguilar D., Allen L.A., Byun J.J., Colvin M.M., Deswal A., Drazner M.H., Dunlay S.M., Evers L.R., et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022;145:e895–e1032. - PubMed
-
- Tsutsui H., Albert N.M., Coats A.J.S., Anker S.D., Bayes-Genis A., Butler J., Chioncel O., Defilippi C.R., Drazner M.H., Felker G.M., et al. Natriuretic Peptides: Role in the Diagnosis and Management of Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement From the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology, Heart Failure Society of America and Japanese Heart Failure Society. J. Card Fail. 2023;29:787–804. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2023.02.009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

