Response Assessment in Brain Metastases Managed by Stereotactic Radiosurgery: A Reappraisal of the RANO-BM Criteria
- PMID: 37999099
- PMCID: PMC10670467
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol30110679
Response Assessment in Brain Metastases Managed by Stereotactic Radiosurgery: A Reappraisal of the RANO-BM Criteria
Abstract
Background: Brain metastases (BM) are increasingly being treated using stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS). Standardized response criteria are necessary to improve research and treatment protocols. This study's goal was to validate the RANO-BM criteria thresholds for tumor progression in a cohort of patients with brain metastases managed using SRS.
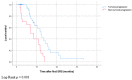
Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of patients treated at least twice with SRS for brain metastases. Local progression, as defined by RANO-BM criteria, was compared to our multidisciplinary tumor board's treatment recommendation. A ROC curve was generated using varying diameter thresholds to assess the sensitivity and specificity of current RANO-BM criteria.
Results: 249 metastases in 67 patients were included in the analysis. RANO-BM criteria current progression thresholds yielded a sensitivity of 38%, a specificity of 95%, a positive predictive value of 71%, and a negative predictive value of 84% relative to our tumor board's treatment recommendation. Modified RANO-BM criteria using absolute diameter differences of 2.5 mm yielded a sensitivity of 83%, a specificity of 87%, a positive predictive value of 67% and a negative predictive value of 94%.
Conclusions: Current RANO-BM criteria unreliably identifies clinically relevant tumor progression. The use of absolute diameter differences thresholds appears superior in our BM cohort.
Keywords: RANO-BM; brain metastases; criteria; diameter; progression; response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Wen P.Y., Loeffler J.S. Management of Brain Metastases. Oncology. 1999;13:941–954. - PubMed
-
- Therasse P., Arbuck S.G., Eisenhauer E.A., Wanders J., Kaplan R.S., Rubinstein L., Verweij J., Van Glabbeke M., van Oosterom A.T., Christian M.C., et al. New Guidelines to Evaluate the Response to Treatment in Solid Tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000;92:205–216. doi: 10.1093/jnci/92.3.205. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

