Stereotactic radiosurgery for noncavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas: treatment outcomes and their predictors
- PMID: 38000078
- PMCID: PMC10810680
- DOI: 10.3171/2023.9.JNS231474
Stereotactic radiosurgery for noncavernous sinus dural arteriovenous fistulas: treatment outcomes and their predictors
Abstract
Objective: Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) has emerged as a safe and effective treatment modality for dural arteriovenous fistulas (dAVFs), particularly cavernous sinus (CS) dAVFs. However, the long-term outcomes of non-CS dAVFs are not well known. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of SRS for non-CS dAVFs and to investigate the risk factors for incomplete obliteration.
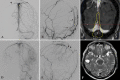
Methods: Between 2007 and 2020, 65 non-CS dAVFs in 63 patients were treated using SRS at a single institution. Demographic characteristics, initial clinical presentations, clinical outcomes, and radiological findings were retrospectively reviewed. The procedure-related complications were assessed. Radiological outcomes were evaluated as complete obliteration, incomplete obliteration, and angiographic worsening, whereas clinical outcomes were evaluated for symptom recovery.
Results: At a median follow-up of 17 months, the overall complete obliteration rate was 63.1%, and the cumulative obliteration rates were 24.6%, 60.0%, 70.0%, and 74.3% at 12, 24, 36, and 48 months, respectively. Six patients underwent retreatment due to angiographic worsening; in 5 of these patients, recruitment of arterial feeders was newly observed in the adjacent sinus, which was not treated in the initial SRS. In the multivariate analysis, high-flow shunt and venous ectasia were associated with incomplete obliteration. No adverse events occurred after SRS.
Conclusions: SRS for non-CS dAVFs is safe, and its efficacy is highly variable according to location. High-flow shunts may indicate greater radioresistance. In the retreated cases, new fistulas tended to be accompanied by sinus steno-occlusion and formed in the adjacent sinus segments.
Keywords: dural arteriovenous fistula; endovascular neurosurgery; noncavernous sinus; stereotactic radiosurgery; vascular disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study or the findings specified in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Borden JA, Wu JK, Shucart WA. A proposed classification for spinal and cranial dural arteriovenous fistulous malformations and implications for treatment. J Neurosurg. 1995;82(2):166–179. - PubMed
-
- Cognard C, Gobin YP, Pierot L, et al. Cerebral dural arteriovenous fistulas: clinical and angiographic correlation with a revised classification of venous drainage. Radiology. 1995;194(3):671–680. - PubMed
-
- Gross BA, Albuquerque FC, Moon K, McDougall CG. Evolution of treatment and a detailed analysis of occlusion, recurrence, and clinical outcomes in an endovascular library of 260 dural arteriovenous fistulas. J Neurosurg. 2017;126(6):1884–1893. - PubMed
-
- Guedin P, Gaillard S, Boulin A, et al. Therapeutic management of intracranial dural arteriovenous shunts with leptomeningeal venous drainage: report of 53 consecutive patients with emphasis on transarterial embolization with acrylic glue. J Neurosurg. 2010;112(3):603–610. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

