The Monarch Initiative in 2024: an analytic platform integrating phenotypes, genes and diseases across species
- PMID: 38000386
- PMCID: PMC10767791
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkad1082
The Monarch Initiative in 2024: an analytic platform integrating phenotypes, genes and diseases across species
Abstract
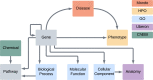
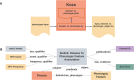
Bridging the gap between genetic variations, environmental determinants, and phenotypic outcomes is critical for supporting clinical diagnosis and understanding mechanisms of diseases. It requires integrating open data at a global scale. The Monarch Initiative advances these goals by developing open ontologies, semantic data models, and knowledge graphs for translational research. The Monarch App is an integrated platform combining data about genes, phenotypes, and diseases across species. Monarch's APIs enable access to carefully curated datasets and advanced analysis tools that support the understanding and diagnosis of disease for diverse applications such as variant prioritization, deep phenotyping, and patient profile-matching. We have migrated our system into a scalable, cloud-based infrastructure; simplified Monarch's data ingestion and knowledge graph integration systems; enhanced data mapping and integration standards; and developed a new user interface with novel search and graph navigation features. Furthermore, we advanced Monarch's analytic tools by developing a customized plugin for OpenAI's ChatGPT to increase the reliability of its responses about phenotypic data, allowing us to interrogate the knowledge in the Monarch graph using state-of-the-art Large Language Models. The resources of the Monarch Initiative can be found at monarchinitiative.org and its corresponding code repository at github.com/monarch-initiative/monarch-app.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures






References
-
- Shefchek K.A., Harris N.L., Gargano M., Matentzoglu N., Unni D., Brush M., Keith D., Conlin T., Vasilevsky N., Zhang X.A.et al. .. The Monarch Initiative in 2019: an integrative data and analytic platform connecting phenotypes to genotypes across species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020; 48:D704–D715. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moxon D., Hannestad S., Mungall L., Bruskiewich C., Bruskiewicz R., Schaper K., Owen K., Solbrig P., Harshad H.et al. .. 2023; biolink/kgx: v2.2.1.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

