Physical activity and checkpoint inhibition: association with toxicity and survival
- PMID: 38001030
- PMCID: PMC10995850
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djad245
Physical activity and checkpoint inhibition: association with toxicity and survival
Abstract
Background: Although animal experiments suggest beneficial effects of physical activity (PA) on antitumor immunity, little is known about the effects of PA on immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) toxicity and effectiveness in humans. We assessed the association of PA with immune-related adverse events (irAE) and survival in patients undergoing ICI.
Methods: Patients receiving ICI who completed the Dutch short questionnaire to assess health enhancing physical activity (SQUASH) questionnaire at the start of treatment as part of the prospective UNICIT study in an academic hospital were included. PA was quantified by calculating total metabolic equivalent task hours per week (total PA) and hours per week of moderate- to vigorous-intensity PA during sport and leisure time (MVPA-SL). Associations of PA with severe irAE occurrence within 1 year and overall survival (OS) were evaluated using logistic regression and Cox proportional hazard regression, respectively, with adjustment for probable confounders.
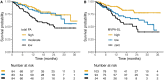
Results: In total, 251 patients were included, with a median follow-up of 20 months. Moderate and high levels of total PA were associated with lower odds of severe irAE occurrence compared to low levels of total PA (adjusted OR: 0.34 [95% CI = 0.12 to 0.90] and 0.19 [95% CI = 0.05 to 0.55], respectively). Moderate and high levels of total PA were also associated with prolonged survival (adjusted HR: 0.58 [95% CI = 0.32 to 1.04] and 0.48 [95% CI = 0.27 to 0.89], respectively). Similar associations were observed in patients who performed more MVPA-SL.
Conclusions: Higher physical activity levels at the start of ICI treatment are associated with lower risk of severe irAEs and probably prolonged survival. Randomized controlled trials are needed to investigate whether patients indeed benefit from increasing PA levels after diagnosis.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Prof. Suijkerbuijk reported grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, TigaTx, and Philips, as well as fees from Bristol Myers Squibb, MSD, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, and AbbVie, Sairopa, paid to institution. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures
References
-
- de Castro G, Kudaba I, Wu YL, et al.Five-year outcomes with pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy as first-line therapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and programmed death ligand-1 tumor proportion score ≥1% in the KEYNOTE-042 study. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41(11):1986-1991. doi:10.1200/JClinOncol.21.02885 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

