Karrikin signalling: impacts on plant development and abiotic stress tolerance
- PMID: 38001035
- PMCID: PMC10860534
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erad476
Karrikin signalling: impacts on plant development and abiotic stress tolerance
Abstract
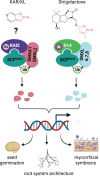
Plants rely upon a diverse range of metabolites to control growth and development, and to overcome stress that results from suboptimal conditions. Karrikins (KARs) are a class of butenolide compounds found in smoke that stimulate seed germination and regulate various developmental processes in plants. KARs are perceived via a plant α/β-hydrolase called KARRIKIN INSENSITIVE2 (KAI2), which also functions as a receptor for a postulated phytohormone, provisionally termed KAI2 ligand (KL). Considered natural analogues of KL, KARs have been extensively studied for their effects on plant growth and their crosstalk with plant hormones. The perception and response pathway for KAR-KL signalling is closely related to that of strigolactones, another class of butenolides with numerous functions in regulating plant growth. KAR-KL signalling influences seed germination, seedling photomorphogenesis, root system architecture, abiotic stress responses, and arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Here, we summarize current knowledge of KAR-KL signalling, focusing on its role in plant development, its effects on stress tolerance, and its interaction with other signalling mechanisms.
Keywords: Abiotic stress; butenolide; development; hormone; karrikin; photomorphogenesis; root architecture; signalling.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Experimental Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abdelrahman M, Mostofa MG, Tran CD, El-Sayed M, Li W, Sulieman S, Tanaka M, Seki M, Tran L-SP.. 2022. The karrikin receptor KARRIKIN INSENSITIVE2 positively regulates heat stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant and Cell Physiology 63, 1914–1926. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama K, Matsuzaki KI, Hayashi H.. 2005. Plant sesquiterpenes induce hyphal branching in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Nature 435, 824–827. - PubMed
-
- Arite T, Umehara M, Ishikawa S, Hanada A, Maekawa M, Yamaguchi S, Kyozuka J.. 2009. d14, a strigolactone-insensitive mutant of rice, shows an accelerated outgrowth of tillers. Plant and Cell Physiology 50, 1416–1424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

