Nanoparticles exhibiting virus-mimic surface topology for enhanced oral delivery
- PMID: 38001086
- PMCID: PMC10673925
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-43465-y
Nanoparticles exhibiting virus-mimic surface topology for enhanced oral delivery
Abstract
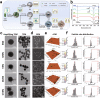
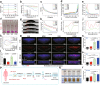
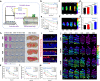
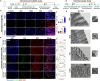
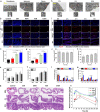
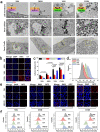
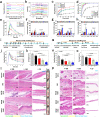
The oral delivery of nano-drug delivery systems (Nano-DDS) remains a challenge. Taking inspirations from viruses, here we construct core-shell mesoporous silica nanoparticles (NPs, ~80 nm) with virus-like nanospikes (VSN) to simulate viral morphology, and further modified VSN with L-alanine (CVSN) to enable chiral recognition for functional bionics. By comparing with the solid silica NPs, mesoporous silica NPs and VSN, we demonstrate the delivery advantages of CVSN on overcoming intestinal sequential barriers in both animals and human via multiple biological processes. Subsequently, we encapsulate indomethacin (IMC) into the nanopores of NPs to mimic gene package, wherein the payloads are isolated from bio-environments and exist in an amorphous form to increase their stability and solubility, while the chiral nanospikes multi-sited anchor and chiral recognize on the intestinal mucosa to enhance the penetrability and ultimately improve the oral adsorption of IMC. Encouragingly, we also prove the versatility of CVSN as oral Nano-DDS.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chiral Nanosilica Drug Delivery Systems Stereoselectively Interacted with the Intestinal Mucosa to Improve the Oral Adsorption of Insoluble Drugs.ACS Nano. 2023 Feb 28;17(4):3705-3722. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c10818. Epub 2023 Feb 14. ACS Nano. 2023. PMID: 36787639
-
Superiority of amino-modified chiral mesoporous silica nanoparticles in delivering indometacin.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018 Aug;46(5):1085-1094. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2017.1360326. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 28776393
-
The On-Off chiral mesoporous silica nanoparticles for delivering achiral drug in chiral environment.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019 Apr 1;176:122-129. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.12.065. Epub 2018 Dec 26. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019. PMID: 30597409
-
Applications of mesoporous materials as excipients for innovative drug delivery and formulation.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(35):6270-89. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319350005. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23470004 Review.
-
Application of commercially available mesoporous silica for drug dissolution enhancement in oral drug delivery.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021 Dec 1;167:106015. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2021.106015. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 34547382 Review.
Cited by
-
Drug delivery systems based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the management of hepatic diseases.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025 Feb;15(2):809-833. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.015. Epub 2024 Dec 20. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025. PMID: 40177563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intestinal nanoparticle delivery and cellular response: a review of the bidirectional nanoparticle-cell interplay in mucosa based on physiochemical properties.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Nov 1;22(1):669. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02930-6. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39487532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial Bacteriophages for Treating Oral Infectious Disease via Localized Bacterial Capture and Enhanced Catalytic Sterilization.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Nov;11(41):e2400394. doi: 10.1002/advs.202400394. Epub 2024 Aug 19. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39159066 Free PMC article.
-
Functionalization of Silica Nanoparticles for Tailored Interactions with Intestinal Cells and Chemical Modulation of Paracellular Permeability.Small Sci. 2024 Aug 1;5(1):2400112. doi: 10.1002/smsc.202400112. eCollection 2025 Jan. Small Sci. 2024. PMID: 40212655 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling dynamics of paramyxovirus-receptor interactions using nanoparticles displaying hemagglutinin-neuraminidase.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Jul 25;20(7):e1012371. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012371. eCollection 2024 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39052678 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

