The ED50 and ED95 of esketamine for preventing early postoperative pain in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a prospective, double-blinded trial
- PMID: 38001477
- PMCID: PMC10675926
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-023-02357-w
The ED50 and ED95 of esketamine for preventing early postoperative pain in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a prospective, double-blinded trial
Abstract
Background: This study aims to estimate the safety, efficacy, and median effective dose (ED50) of esketamine for preventing early postoperative pain in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
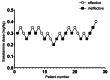
Methods: 54 patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy were prospectively randomized into two groups (group C and group E). Different doses of esketamine were intravenously administered before the skin incision in Group E. The patients in group C received the same dose of saline at the same time. General population characteristics were recorded. The median effective dose (ED50) and 95% effective dose (ED95) were calculated using Dixon's up-and-down method. Hemodynamic parameters were monitored, and pain intensity was assessed using a visual analog scale. We also recorded the condition of anesthesia recovery period and postoperative adverse reactions.
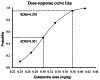
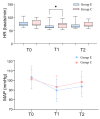
Results: The ED50 of esketamine for preventing early postoperative pain was 0.301 mg/kg (95%CI: 0.265-0.342 mg/kg), and the ED95 was 0.379 mg/kg (95%CI: 0.340-0.618 mg/kg), calculated by probability unit regression. Heart rate (HR) was significantly lower in the esketamine group compared to the control at the skin incision (p < 0.05). The total VAS score at resting was significantly lower in the esketamine group compared to the control group during the awakening period (p < 0.05). There was no significant difference between the two groups regarding the incidence of adverse reactions (p > 0.05).
Conclusions: In this study, esketamine can prevent early postoperative pain effectively. The ED50 and ED95 of esketamine for controlling early postoperative pain were 0.301 mg/kg and 0.379 mg/kg, respectively.
Trial registration: ChiCTR2200066663, 13/12/2022.
Keywords: ED50; ED95; Esketamine; Laparoscopic cholecystectomy; Postoperative pain.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Establishing the Median and 95% Effective Doses of Oliceridine for Immediate Post-Surgical Analgesia Following Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Double-Blind, Sequential Dose-Finding Study.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Apr 8;19:2737-2747. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S505079. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40226130 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Determining the effective dose of esketamine for mitigating pain during propofol injection by Dixon's up-and-down method: a double-blind, prospective clinical study of drug dose response.BMC Anesthesiol. 2022 Dec 1;22(1):368. doi: 10.1186/s12871-022-01914-z. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022. PMID: 36457068 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effective doses of remimazolam and esketamine combined with remifentanil for endotracheal intubation without muscle relaxants in pediatric patients.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 18;16:1558966. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1558966. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40170717 Free PMC article.
-
The ED50 and ED95 of ketamine for prevention of postoperative hyperalgesia after remifentanil-based anaesthesia in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy.Swiss Med Wkly. 2011 May 10;141:w13195. doi: 10.4414/smw.2011.13195. eCollection 2011. Swiss Med Wkly. 2011. PMID: 21557114 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison Between Esketamine and Alfentanil for Hysteroscopy: A Prospective, Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Trial.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Aug 14;18:3629-3641. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S472651. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39161682 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of subanaesthetic esketamine on the prevention of postoperative delirium in older adult patients after cardiovascular surgery: protocol for a single-centre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (SEPDOC trial) in China.BMJ Open. 2025 Jun 16;15(6):e089719. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-089719. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40523785 Free PMC article.
-
Establishing the Median and 95% Effective Doses of Oliceridine for Immediate Post-Surgical Analgesia Following Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: A Double-Blind, Sequential Dose-Finding Study.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Apr 8;19:2737-2747. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S505079. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40226130 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Preemptive hydromorphone analgesia reduces postoperative delirium and stress response in laparoscopic cholecystectomy patients.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Dec 15;16(12):7427-7437. doi: 10.62347/HFRZ2901. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39822504 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Remimazolam Tosilate Combined with Esketamine on Anesthetic Efficacy and Psychiatric Symptoms in Patients Undergoing Ambulatory Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Study.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 May 30;19:4527-4535. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S519732. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40464034 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Hang LH, Shao DH, Gu YP. The ED50 and ED95 of ketamine for prevention of postoperative hyperalgesia after remifentanil-based anaesthesia in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Swiss Med Wkly. 2011;141:w13195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

