Plasma exosomes improve peripheral neuropathy via miR-20b-3p/Stat3 in type I diabetic rats
- PMID: 38001489
- PMCID: PMC10675980
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-023-02222-5
Plasma exosomes improve peripheral neuropathy via miR-20b-3p/Stat3 in type I diabetic rats
Abstract
Background: Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is one of the most common complications of diabetes and the main cause of non-traumatic amputation, with no ideal treatment. Multiple cell-derived exosomes have been reported to improve the progression of DPN. Blood therapy is thought to have a powerful repairing effect. However, whether it could also improve DPN remains unclear.
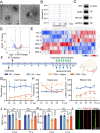
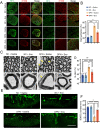
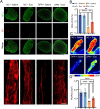
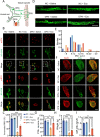
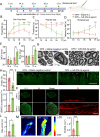
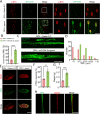
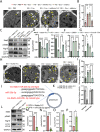
Results: In this study, we found that microRNA (miRNA) expression in plasma-derived exosomes of healthy rats (hplasma-exos) was significantly different from that of age-matched DPN rats. By injection of hplasma-exos into DPN rats, the mechanical sensitivity of DPN rats was decreased, the thermal sensitivity and motor ability were increased, and the nerve conduction speed was accelerated. Histological analysis showed myelin regeneration of the sciatic nerve, increased intraepidermal nerve fibers, distal local blood perfusion, and enhanced neuromuscular junction and muscle spindle innervation after hplasma-exos administration. Compared with plasma exosomes in DPN, miR-20b-3p was specifically enriched in exosomes of healthy plasma and was found to be re-upregulated in the sciatic nerve of DPN rats after hplasma-exos treatment. Moreover, miR-20b-3p agomir improved DPN symptoms to a level similar to hplasma-exos, both of which also alleviated autophagy impairment induced by high glucose in Schwann cells. Mechanistic studies found that miR-20b-3p targeted Stat3 and consequently reduced the amount of p-Stat3, which then negatively regulated autophagy processes and contributed to DPN improvement.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that miRNA of plasma exosomes was different between DPN and age-matched healthy rats. MiR-20b-3p was enriched in hplasma-exos, and both of them could alleviated DPN symptoms. MiR-20b-3p regulated autophagy of Schwann cells in pathological states by targeting Stat3 and thereby inhibited the progression of DPN.
Keywords: Autophagy; Diabetic peripheral neuropathy; Plasma exosomes; miRNAs.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cell-derived exosome therapy for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a preclinical animal studies systematic review and meta-analysis.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Jun 9;16(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04432-0. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40490808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes ameliorate peripheral neuropathy in a mouse model of diabetes.Diabetologia. 2020 Feb;63(2):431-443. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-05043-0. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Diabetologia. 2020. PMID: 31740984 Free PMC article.
-
Increased BMSC exosomal miR-140-3p alleviates bone degradation and promotes bone restoration by targeting Plxnb1 in diabetic rats.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Mar 2;20(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01267-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35236339 Free PMC article.
-
Astragaloside IV alleviates Schwann cell injury in diabetic peripheral neuropathy by regulating microRNA-155-mediated autophagy.Phytomedicine. 2021 Nov;92:153749. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153749. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34601220
-
Exploring the role of exosomes in diabetic neuropathy: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic potential.Biomed Pharmacother. 2025 Apr;185:117959. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2025.117959. Epub 2025 Mar 8. Biomed Pharmacother. 2025. PMID: 40056828 Review.
Cited by
-
Autophagy in Schwann cells: A potential pharmacotherapeutic target in diabetic peripheral neuropathy.World J Diabetes. 2025 Jun 15;16(6):105709. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i6.105709. World J Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 40548273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Application of Stem Cells and Exosomes in Promoting Nerve Conduits for Peripheral Nerve Repair.Biomater Res. 2025 Apr 14;29:0160. doi: 10.34133/bmr.0160. eCollection 2025. Biomater Res. 2025. PMID: 40231207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-derived exosome therapy for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a preclinical animal studies systematic review and meta-analysis.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Jun 9;16(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04432-0. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40490808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of NGF-enriched extracellular vesicles in modulating neuroinflammation and enhancing peripheral nerve remyelination.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2025 May 27;13(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s40478-025-02033-9. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2025. PMID: 40420167 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes from young plasma stimulate the osteogenic differentiation and prevent osteoporosis via miR-142-5p.Bioact Mater. 2025 Mar 20;49:502-514. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.03.012. eCollection 2025 Jul. Bioact Mater. 2025. PMID: 40206195 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82271414/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- YDZJ202301ZYTS017/Jilin Provincial Scientific and Technological Development Program
- 2022SCZ24/Special Project on Health Talents of Jilin Province
- 2023CL05/Spring Bud Program of China-Japan Union Hospital of Jilin University
- 2023B19/Bethune Project of Jilin University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

