Immune thrombocytopenic purpura after influenza vaccine administration; a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38001495
- PMCID: PMC10675976
- DOI: 10.1186/s40794-023-00206-9
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura after influenza vaccine administration; a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The American Society of Haematology defines immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) as a common hematologic disorder characterized by a transient or long-term decrease in platelet counts (< 100 × 109/L.), purpura, and haemorrhagic episodes caused by antiplatelet autoantibodies, with the exclusion of other clinical conditions. We aimed to systematically determine the incidence of ITP in adults and children following influenza vaccination, the duration between vaccination and the occurrence of ITP, and to identify predictors of ITP after the vaccine.
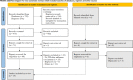
Methods: We searched PubMed, Cochrane Library, Google Scholar, Web of Science, Scopus, and Science Direct. We included primary studies that assessed the occurrence of immune thrombocytopenia in individuals who had received any influenza vaccine (primary or booster dose), regardless of the dosage, preparation, time of administration, or age of the participants. We excluded studies that were (a) Narrative, scoping, and umbrella reviews ;(b) studies with no accessible full text, abstract-only studies, or (c) Overlapping or unreliable data. The risk of bias in the included studies was assessed using the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) tool. We categorized studies for qualitative analysis based on study design. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize quantitative data, including the incidence of ITP after influenza vaccination.
Results: Out of 729 articles retrieved from the database search, we included 24 studies. All patients identified and included in this systematic review presented with immune thrombocytopenia, determined by their platelet count. The period between vaccination and the occurrence of ITP ranged from (2:35 days). The mean duration was 13.5 days. The analysis revealed a statistically significant incidence rate ratio (IRR) = 1.85,95% CI [1.03-3.32] of ITP occurrence after 42 days.
Conclusions: Influenza-associated ITP is uncommon, self-limiting, non-life-threatening, and curable. None of the patients reported having severe adverse events or death. Further studies are required to confirm the exact incidence of the ITP to better understand the pathophysiology of ITP development post-influenza vaccination.
Keywords: Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP); Influenza vaccine; Meta-analysis.; Platelets; Systematic review.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The potential impact of COVID-19 vaccination on patients with immune thrombocytopenic purpura: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Nov 11;19(11):e0308546. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308546. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39527538 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Influenza Vaccine and Immune Thrombocytopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Nov 20;12(11):1298. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12111298. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39591200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The sensitivity and specificity of platelet autoantibody testing in immune thrombocytopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of a diagnostic test.J Thromb Haemost. 2019 May;17(5):787-794. doi: 10.1111/jth.14419. Epub 2019 Mar 20. J Thromb Haemost. 2019. PMID: 30801909
-
[Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in children].Med Pregl. 1998 Mar-Apr;51(3-4):127-34. Med Pregl. 1998. PMID: 9611955 Review. Croatian.
-
Romiplostim in chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura.Clin Ther. 2009 Sep;31(9):1887-907. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2009.09.013. Clin Ther. 2009. PMID: 19843480 Review.
References
-
- Zufferey A, Kapur R, Semple J. Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Mechanisms in Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP). J Clin Med [Internet]. 2017;6(2):16. Available from: http://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/6/2/16.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources