MicroRNA Profiling of Red Blood Cells for Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- PMID: 38001571
- PMCID: PMC10670279
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15225312
MicroRNA Profiling of Red Blood Cells for Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Abstract
Background: Despite extensive endeavors to establish cell-free circulating biomarkers for lung cancer diagnosis, clinical adoption remains elusive. Noteworthy, emergent evidence suggests the pivotal roles of red blood cells (RBCs) and their derivatives in tumorigenesis, illuminating potential avenues for diagnostic advancements using blood cell-derived microRNAs (miRNAs).
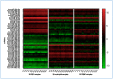
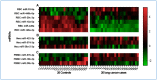
Methods: We executed microarray analyses on three principal blood cell types-RBCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), and neutrophils-encompassing 26 lung cancer patients and 26 healthy controls. Validation was performed using droplet digital PCR within an additional cohort comprising 42 lung cancer and 39 control cases.
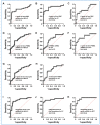
Results: Our investigation unearthed distinct miRNA profiles associated with lung cancer across all examined blood cell types. Intriguingly, RBC-miRNAs emerged as potential novel biomarkers for lung cancer, an observation yet to be documented. Importantly, integrating miRNAs from disparate blood cell types yielded a superior diagnostic accuracy for lung cancer over individual cell-type miRNAs. Subsequently, we formulated three diagnostic panels, adeptly discerning non-small cell lung cancer, adenocarcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma, maintaining consistency across various disease stages.
Conclusion: RBC-derived molecules introduce novel cancer biomarkers, and exploiting miRNA profiles across varied blood cell types unveils a promising frontier for lung cancer's early detection and histological classification.
Keywords: biomarkers; diagnosis; lung cancer; miRNAs; red blood cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-based biomarkers for diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Thorac Cancer. 2020 Mar;11(3):762-768. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13337. Epub 2020 Jan 28. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31994346 Free PMC article.
-
Differential miRNA expressions in peripheral blood mononuclear cells for diagnosis of lung cancer.Lab Invest. 2015 Oct;95(10):1197-206. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2015.88. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Lab Invest. 2015. PMID: 26146958 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Tumor-Derived Exosomal miRNA as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Next-Generation Sequencing.Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Sep 1;23(17):5311-5319. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-0577. Epub 2017 Jun 12. Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28606918
-
miRNAs in lung cancer. A systematic review identifies predictive and prognostic miRNA candidates for precision medicine in lung cancer.Transl Res. 2021 Apr;230:164-196. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2020.11.012. Epub 2020 Nov 28. Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 33253979
-
Small RNA Deep Sequencing of Circulating Small RNAs Discovers a Unique Panel of microRNAs as Feasible and Reliable Biomarkers of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers in Northern Thailand.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023 Oct 1;24(10):3585-3598. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2023.24.10.3585. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2023. PMID: 37898867 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the role of blood cell perturbation responses in lung cancer by Mendelian randomization.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jun 15;16(1):1111. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02821-8. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40517349 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting mir-155-3p through a Molecular Beacon Bead-Based Assay.Molecules. 2024 Jul 3;29(13):3182. doi: 10.3390/molecules29133182. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38999134 Free PMC article.
-
Red blood cells could protect miRNAs from degradation or loss thanks to Argonaute 2 binding.FEBS Open Bio. 2025 May;15(5):810-821. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.70005. Epub 2025 Apr 15. FEBS Open Bio. 2025. PMID: 40235152 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arroyo J.D., Chevillet J.R., Kroh E.M., Ruf I.K., Pritchard C.C., Gibson D.F., Mitchell P.S., Bennett C.F., Pogosova-Agadjanyan E.L., Stirewalt D.L., et al. Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2011;108:5003–5008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1019055108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

