Amivantamab Compared with Real-World Physician's Choice after Platinum-Based Therapy from a Pan-European Chart Review of Patients with Lung Cancer and Activating EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations
- PMID: 38001589
- PMCID: PMC10670157
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15225326
Amivantamab Compared with Real-World Physician's Choice after Platinum-Based Therapy from a Pan-European Chart Review of Patients with Lung Cancer and Activating EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations
Abstract
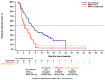
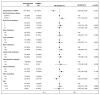
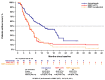
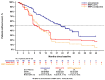
Patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with epidermal growth factor receptor gene (EGFR) Exon 20 insertions (Exon20ins) at the second line and beyond (2L+) have an unmet need for new treatment. Amivantamab, a bispecific EGFR- and MET-targeted antibody, demonstrated efficacy in this setting in the phase 1b, open-label CHRYSALIS trial (NCT02609776). The primary objective was to compare the efficacy of amivantamab to the choices made by real-world physicians (RWPC) using an external control cohort from the real-world evidence (RWE) chart review study, CATERPILLAR-RWE. Adjustment was conducted to address differences in prognostic variables between cohorts using inverse probability weighting (IPW) and covariate adjustments based on multivariable regression. In total, 114 patients from CHRYSALIS were compared for 55 lines of therapy from CATERPILLAR-RWE. Baseline characteristics were comparable between the amivantamab and IPW-weighted RWPC cohorts. For amivantamab versus RWPC using IPW adjustment, the response rate ratio for the overall response was 2.14 (p = 0.0181), and the progression-free survival (PFS), time-to-next-treatment (TTNT) and overall survival (OS) hazard ratios (HRs) were 0.42 (p < 0.0001), 0.47 (p = 0.0063) and 0.48 (p = 0.0207), respectively. These analyses provide evidence of clinical and statistical benefits across multiple outcomes and adjustment methods, of amivantamab in platinum pre-treated patients with advanced NSCLC harboring EGFR Exon20ins. These results confirm earlier comparisons versus pooled national registry data.
Keywords: EGFR Exon 20 insertion mutations; adjusted comparison; amivantamab; non-small cell lung cancer; real-world physician’s choice.
Conflict of interest statement
As stated above, this research was funded by Janssen Pharmaceutica NV. All Janssen authors contributed to the design of the study, the collection, analysis and interpretation of data, the writing of the manuscript, and the decision to publish the results. Petros Christopoulos: Research funding from AstraZeneca, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Roche, and Takeda; advisory board/speaker’s honoraria from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Takeda, and Thermo Fisher; all outside the submitted work. Nicolas Girard: Consulting/advisory role for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, PharmaMar, Roche, Sanofi, and Takeda; travel, accommodations, expenses for AstraZeneca, BMS, MSD Oncology, and Roche; research funding from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Roche. Claudia Proto: Consulting/advisory role for AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, MSD, Roche, and Sanofi; travel, accommodation, expenses for AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD, and Roche; institutional research funding from AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly Roche, MSD, Spectrum Pharmaceutical, Janssen, and Pfizer. Marta Soares: Consulting/advisory role for AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim Janssen, Eli Lilly, Merck Serono, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and Takeda. Pilar Garrido Lopez: Consultancy/honoraria from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, and Takeda; direct funding from Medscape and Touch Medical; institutional research funding from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Blueprint, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, IO Biotech, MSD, Roche, and Takeda. Anthonie J. van der Wekken: Grants and personal fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Pfizer, Roche, and Takeda; personal fees from Amgen, Lilly, and Merck; outside the submitted work and all payments to the UMCG. Sanjay Popat: Consultancy/honoraria from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BeiGene, Blueprint, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, EQRx, GlaxoSmithKline, Guardant Health, Janssen, Merck KGaA, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, Seattle Genetics, Takeda, and Turning Point Therapeutics; direct funding from Elsevier, Medscape, Touch Medical, and VJ Oncology; institutional research funding from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Blueprint, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Guardant Health, Janssen, MSD, Roche, Takeda, Seattle Genetics, Trizel, and Turning Point Therapeutics. Joris Diels: Employee of Janssen and shareholder of Johnson & Johnson. Claudio A. Schioppa: Employee of Janssen and shareholder of Johnson & Johnson. Jan Sermon: Employee of Janssen and shareholder of Johnson & Johnson. Nora Rahhali: Employee of Janssen and shareholder of Johnson & Johnson. Corinna Pick-Lauer: Employee of Janssen. Agnieszka Adamczyk: Employee of Janssen and shareholder of Johnson & Johnson. James Penton: Employee of Janssen and shareholder of Johnson & Johnson. Marie Wislez: Consulting/advisory role from AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and Takeda; travel, accommodations, expenses from AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD, and Roche.
Figures



Similar articles
-
An Adjusted Treatment Comparison Comparing Amivantamab Versus Real-World Clinical Practice in Europe and the United States for Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Activating Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Exon 20 Insertion Mutations.Adv Ther. 2023 Mar;40(3):1187-1203. doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02408-7. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Adv Ther. 2023. PMID: 36652175 Free PMC article.
-
Amivantamab compared with real-world therapies in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer EGFR Exon 20 insertion mutations after platinum-based chemotherapy.Acta Oncol. 2023 Dec;62(12):1689-1697. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2023.2254479. Epub 2023 Nov 25. Acta Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37938161
-
Amivantamab compared with real-world therapies in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations who progressed after platinum-based chemotherapy.Lung Cancer. 2022 Jun;168:74-82. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2022.03.005. Epub 2022 Mar 8. Lung Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35597172
-
Amivantamab-Vmjw: A Novel Treatment for Patients with NSCLC Harboring EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutation after Progression on Platinum-Based Chemotherapy.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 20;11(3):950. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030950. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amivantamab in the Treatment of Metastatic NSCLC: Patient Selection and Special Considerations.Onco Targets Ther. 2022 Oct 12;15:1197-1210. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S329095. eCollection 2022. Onco Targets Ther. 2022. PMID: 36246734 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Riess J.W., Gandara D.R., Frampton G.M., Madison R., Peled N., Bufill J.A., Dy G.K., Ou S.I., Stephens P.J., McPherson J.D., et al. Diverse EGFR Exon 20 Insertions and Co-Occurring Molecular Alterations Identified by Comprehensive Genomic Profiling of NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018;13:1560–1568. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2018.06.019. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

