Antiproliferative Modulation and Pro-Apoptotic Effect of BR2 Tumor-Penetrating Peptide Formulation 2-Aminoethyl Dihydrogen Phosphate in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 38001606
- PMCID: PMC10670255
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15225342
Antiproliferative Modulation and Pro-Apoptotic Effect of BR2 Tumor-Penetrating Peptide Formulation 2-Aminoethyl Dihydrogen Phosphate in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
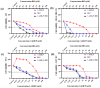
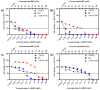
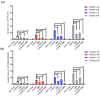
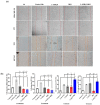
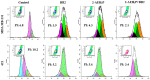
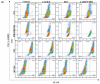
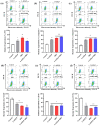
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women, the so-called "Triple-Negative Breast Cancer" (TNBC) subtype remaining the most challenging to treat, with low tumor-free survival and poor clinical evolution. Therefore, there is a clear medical need for innovative and more efficient treatment options for TNBC. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the potential therapeutic interest of the association of the tumor-penetrating BR2 peptide with monophosphoester 2-aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate (2-AEH2P), a monophosphoester involved in cell membrane turnover, in TNBC. For that purpose, viability, migration, proliferative capacity, and gene expression analysis of proteins involved in the control of proliferation and apoptosis were evaluated upon treatment of an array of TNBC cells with the BR2 peptide and 2-AEH2P, either separately or combined. Our data showed that, while possessing limited single-agent activity, the 2-AEH2P+BR2 association promoted significant cytotoxicity in TNBC cells but not in normal cells, with reduced proliferative potential and inhibition of cell migration. Mechanically, the 2-AEH2P+BR2 combination promoted an increase in cells expressing p53 caspase 3 and caspase 8, a reduction in cells expressing tumor progression and metastasis markers such as VEGF and PCNA, as well as a reduction in mitochondrial electrical potential. Our results indicate that the combination of the BR2 peptide with 2-AEH2P+BR2 may represent a promising therapeutic strategy in TNBC with potential use in clinical settings.
Keywords: monophosphoester; nano therapy; peptide; triple-negative breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Ministerio da Saúde . Incidencia de Câncer no Brasil. Volume 1. Instituto Nacional do Câncer José de Alencar Gomes da Silva; Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: 2020. pp. 1–122.
-
- Lin N.U., Claus E., Sohl J., Razzak A.R., Arnaout A., Winer E.P. Sites of distant recurrence and clinical outcomes in patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: High incidence of central nervous system metastases. Cancer. 2008;113:2638–2645. doi: 10.1002/cncr.23930. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

