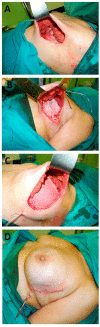
Single-Stage Immediate Breast Reconstruction with Acellular Dermal Matrix after Breast Cancer: Comparative Study and Evaluation of Breast Reconstruction Outcomes
- PMID: 38001609
- PMCID: PMC10670310
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15225349
Single-Stage Immediate Breast Reconstruction with Acellular Dermal Matrix after Breast Cancer: Comparative Study and Evaluation of Breast Reconstruction Outcomes
Abstract
We evaluate postoperative complications, aesthetic results and satisfaction outcomes in patients with breast cancer after intervening with a skin-sparing or nipple-sparing mastectomy with an immediate prosthetic reconstruction with or without a biological mesh. Patients with multifocal breast cancer, ductal carcinoma in situ with an indication for a mastectomy and cT2 tumors with no response to primary systemic treatment were included, whereas patients aged >75 years, with inflammatory carcinoma, and severe circulatory disorders were excluded. Patients in the control group were reconstructed using a prosthesis, whereas the study group included patients reconstructed using a prosthesis and biological acellular porcine dermal mesh (Strattice™). In both groups, the result was assessed using the BREAST-Q instrument. A total of 51 patients (62 intervened breasts) were included in the study group and 38 patients (41 intervened breasts) in the control group. Implant loss and removal occurred in three patients in the study group (5.9%) and nine patients in the control group (24.3%; p = 0.030). Infections appeared in three patients in the study group (4.8%) and three patients in the control group (7.3%; p = 1.00). Skin necrosis appeared in 5 patients in the study group (12.2%) and 11 patients in the control group (21.6%; p = 0.367). Seroma appeared in five patients in the study group (12.2%) and five patients in the control group (8.1%; p = 0.514). The BREAST-Q questionnaire is a comparison between both groups regarding "satisfaction with breasts after surgery" (p = 0.026), "sexual well-being after intervention" (p = 0.010) and "satisfaction with the information received" (p = 0.049). We have noted a statistically significant decrease in implant loss in women receiving an implant with a biological mesh. A higher satisfaction was observed in patients reconstructed using Strattice™, with statistically significant differences in three items.
Keywords: BREAST-Q questionnaire; biological mesh; breast cancer; immediate reconstruction; skin-sparing mastectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Implant-based immediate reconstruction in prophylactic mastectomy: is the caudal dermis flap a reliable alternative to synthetic mesh or acellular dermal matrix?Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2022 Apr;305(4):937-943. doi: 10.1007/s00404-021-06244-y. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2022. PMID: 34554314 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Study of Nipple-Areola Complex Position and Patient Satisfaction After Unilateral Mastectomy and Immediate Expander-Implant Reconstruction Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy Versus Skin-Sparing Mastectomy.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2019 Apr;43(2):313-327. doi: 10.1007/s00266-018-1217-8. Epub 2019 Feb 11. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2019. PMID: 30746565
-
Quality of Life and Early Functional Evaluation in Direct-to-Implant Breast Reconstruction After Mastectomy: A Comparative Study Between Prepectoral Versus Dual-Plane Reconstruction.Clin Breast Cancer. 2021 Aug;21(4):344-351. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2020.11.013. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Clin Breast Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33308993
-
Porcine Acellular Peritoneal Matrix in Immediate Breast Reconstruction: A Multicenter, Prospective, Single-Arm Trial.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019 Jan;143(1):10e-21e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000005095. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019. PMID: 30589773 Clinical Trial.
-
Indocyanine green angiography for preventing postoperative mastectomy skin flap necrosis in immediate breast reconstruction.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Apr 22;4(4):CD013280. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013280.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32320056 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Decellularized porcine dermal hydrogel enhances implant-based wound healing in the setting of irradiation.Acta Biomater. 2025 Jan 1;191:260-275. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2024.11.009. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Acta Biomater. 2025. PMID: 39522628
-
Types of Breast Cancer Surgery and Breast Reconstruction.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Sep 20;16(18):3212. doi: 10.3390/cancers16183212. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335183 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xu H., Wan H., Zuo W., Sun W., Owens R.T., Harper J.R., Ayares D.L., McQuillan D.J. A Porcine-Derived Acellular Dermal Scaffold That Supports Soft Tissue Regeneration: Removal of Terminal Galactose-alpha-(1,3)-Galactose and Retention of Matrix Structure. Tissue Eng. Part A. 2009;15:1807–1819. doi: 10.1089/ten.tea.2008.0384. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources