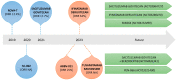
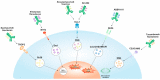
Unlocking New Horizons in Small-Cell Lung Cancer Treatment: The Onset of Antibody-Drug Conjugates
- PMID: 38001628
- PMCID: PMC10670928
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15225368
Unlocking New Horizons in Small-Cell Lung Cancer Treatment: The Onset of Antibody-Drug Conjugates
Abstract
Small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a highly aggressive disease, accounting for about 15% of all lung cancer cases. Despite initial responses to chemoimmunotherapy, SCLC recurs and becomes resistant to treatment. Recently, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) have emerged as a promising therapeutic option for SCLC. ADCs consist of an antibody that specifically targets a tumor antigen linked to a cytotoxic drug. The antibody delivers the drug directly to the cancer cells, minimizing off-target toxicity and improving the therapeutic index. Several ADCs targeting different tumor antigens are currently being evaluated in clinical trials for SCLC. Despite the negative results of rovalpituzumab tesirine (Rova-T), other ADCs targeting different antigens, such as B7-H3, seizure-related homolog 6 (SEZ6), and CEACAM5, have also been investigated in clinical trials, including for SCLC, and their results suggest preliminary activity, either alone or in combination with other therapies. More recently, sacituzumab govitecan, an anti-TROP2 ADC, demonstrated promising activity in lung cancer, including SCLC. Furthermore, an anti-B7-H3 (CD276), ifinatamab deruxtecan (DS7300A), showed a high response rate and durable responses in heavily pretreated SCLC. Overall, ADCs represent an intriguing approach to treating SCLC, particularly in the relapsed or refractory setting. Further studies are needed to determine their efficacy and safety and the best location in the treatment algorithm for SCLC. In this review, we aim to collect and describe the results regarding the past, the present, and the future of ADCs in SCLC.
Keywords: ADCs; CEACAM5; DLL3; SCLC; TROP2.
Conflict of interest statement
L.B. received speakers’ fees from Astra-Zeneca, MSD, Roche, and Takeda outside the submitted manuscript; travel fees were from Takeda. A.R. has stock options from IQVIA Holdings Inc. S.P. received honoraria or speakers’ fees from Astra-Zeneca, Eli-Lilly, BMS, MSD, Takeda, Amgen, Novartis, and Roche, outside the submitted manuscript. L.C. received speakers’ fees from Eli-Lilly, Novartis, and Astra-Zeneca. All remaining authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Liu S.V., Reck M., Mansfield A.S., Mok T., Scherpereel A., Reinmuth N., Garassino M.C., De Castro Carpeno J., Califano R., Nishio M., et al. Updated Overall Survival and PD-L1 Subgroup Analysis of Patients With Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer Treated With Atezolizumab, Carboplatin, and Etoposide (IMpower133) J. Clin. Oncol. 2021;39:619–630. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.01055. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Paz-Ares L., Chen Y., Reinmuth N., Hotta K., Trukhin D., Statsenko G., Hochmair M.J., Özgüroğlu M., Ji J.H., Garassino M.C., et al. Durvalumab, with or without tremelimumab, plus platinum-etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: 3-year overall survival update from CASPIAN. ESMO Open. 2022;7:100408. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2022.100408. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abdollahpour-Alitappeh M., Lotfinia M., Gharibi T., Mardaneh J., Farhadihosseinabadi B., Larki P., Faghfourian B., Sepehr K.S., Abbaszadeh-Goudarzi K., Abbaszadeh-Goudarzi G., et al. Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) for cancer therapy: Strategies, challenges, and successes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019;234:5628–5642. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27419. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous