The Important Role of Protein Kinases in the p53 Sestrin Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 38001650
- PMCID: PMC10670278
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15225390
The Important Role of Protein Kinases in the p53 Sestrin Signaling Pathway
Abstract
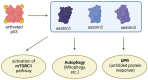
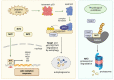
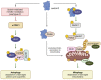
p53, a crucial tumor suppressor and transcription factor, plays a central role in the maintenance of genomic stability and the orchestration of cellular responses such as apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and DNA repair in the face of various stresses. Sestrins, a group of evolutionarily conserved proteins, serve as pivotal mediators connecting p53 to kinase-regulated anti-stress responses, with Sestrin 2 being the most extensively studied member of this protein family. These responses involve the downregulation of cell proliferation, adaptation to shifts in nutrient availability, enhancement of antioxidant defenses, promotion of autophagy/mitophagy, and the clearing of misfolded proteins. Inhibition of the mTORC1 complex by Sestrins reduces cellular proliferation, while Sestrin-dependent activation of AMP-activated kinase (AMPK) and mTORC2 supports metabolic adaptation. Furthermore, Sestrin-induced AMPK and Unc-51-like protein kinase 1 (ULK1) activation regulates autophagy/mitophagy, facilitating the removal of damaged organelles. Moreover, AMPK and ULK1 are involved in adaptation to changing metabolic conditions. ULK1 stabilizes nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), thereby activating antioxidative defenses. An understanding of the intricate network involving p53, Sestrins, and kinases holds significant potential for targeted therapeutic interventions, particularly in pathologies like cancer, where the regulatory pathways governed by p53 are often disrupted.
Keywords: Sestrins; autophagy; mTORC; mitophagy; nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2); p53; stress response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The antioxidant function of sestrins is mediated by promotion of autophagic degradation of Keap1 and Nrf2 activation and by inhibition of mTORC1.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Nov;88(Pt B):205-211. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.06.007. Epub 2015 Jun 25. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 26117317 Review.
-
Cardioprotective roles of sestrin 1 and sestrin 2 against doxorubicin cardiotoxicity.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019 Jul 1;317(1):H39-H48. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00008.2019. Epub 2019 Apr 26. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31026186 Free PMC article.
-
Quercetin regulates the sestrin 2-AMPK-p38 MAPK signaling pathway and induces apoptosis by increasing the generation of intracellular ROS in a p53-independent manner.Int J Mol Med. 2014 Apr;33(4):863-9. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1658. Epub 2014 Feb 13. Int J Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24535669 Free PMC article.
-
SQSTM1/p62 activates NFE2L2/NRF2 via ULK1-mediated autophagic KEAP1 degradation and protects mouse liver from lipotoxicity.Autophagy. 2020 Nov;16(11):1949-1973. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1712108. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Autophagy. 2020. PMID: 31913745 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy in the physiological endometrium and cancer.Autophagy. 2021 May;17(5):1077-1095. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1752548. Epub 2020 May 13. Autophagy. 2021. PMID: 32401642 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integration analysis of microRNAs as potential biomarkers in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma: the diagnostic and therapeutic significance of miR-183-3p.Front Oncol. 2024 Dec 17;14:1508715. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1508715. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39759146 Free PMC article.
-
[Research and Therapeutic Advances of 26S Proteasome Subunit in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2025 May 20;28(5):363-370. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2025.106.13. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40506490 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Living on the Edge: ROS Homeostasis in Cancer Cells and Its Potential as a Therapeutic Target.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Aug 16;14(8):1002. doi: 10.3390/antiox14081002. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40867898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in T Lymphocyte Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 1;25(11):6114. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116114. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding the molecular symphony: interactions between the m6A and p53 signaling pathways in cancer.NAR Cancer. 2024 Sep 26;6(3):zcae037. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcae037. eCollection 2024 Sep. NAR Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39329012 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

