Integrins Can Act as Suppressors of Ras-Mediated Oncogenesis in the Drosophila Wing Disc Epithelium
- PMID: 38001693
- PMCID: PMC10670217
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15225432
Integrins Can Act as Suppressors of Ras-Mediated Oncogenesis in the Drosophila Wing Disc Epithelium
Abstract
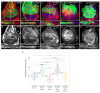
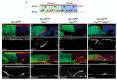
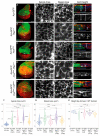
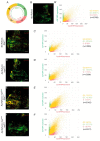
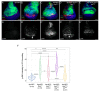
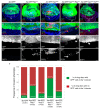
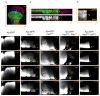
Cancer is the second leading cause of death worldwide. Key to cancer initiation and progression is the crosstalk between cancer cells and their microenvironment. The extracellular matrix (ECM) is a major component of the tumour microenvironment and integrins, main cell-ECM adhesion receptors, are involved in every step of cancer progression. However, accumulating evidence has shown that integrins can act as tumour promoters but also as tumour suppressor factors, revealing that the biological roles of integrins in cancer are complex. This incites a better understating of integrin function in cancer progression. To achieve this goal, simple model organisms, such as Drosophila, offer great potential to unravel underlying conceptual principles. Here, we find that in the Drosophila wing disc epithelium the βPS integrins act as suppressors of tumours induced by a gain of function of the oncogenic form of Ras, RasV12. We show that βPS integrin depletion enhances the growth, delamination and invasive behaviour of RasV12 tumour cells, as well as their ability to affect the tumour microenvironment. These results strongly suggest that integrin function as tumour suppressors might be evolutionarily conserved. Drosophila can be used to understand the complex tumour modulating activities conferred by integrins, thus facilitating drug development.
Keywords: Drosophila integrins; cancer; cell growth; invasion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrins Cooperate With the EGFR/Ras Pathway to Preserve Epithelia Survival and Architecture in Development and Oncogenesis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jun 13;10:892691. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.892691. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35769262 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial regulation of cell adhesion in the Drosophila wing is mediated by Delilah, a potent activator of βPS integrin expression.Dev Biol. 2011 Mar 1;351(1):99-109. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.12.039. Epub 2011 Jan 4. Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21215259
-
Drosophila as Model System to Study Ras-Mediated Oncogenesis: The Case of the Tensin Family of Proteins.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jul 23;14(7):1502. doi: 10.3390/genes14071502. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510408 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin control of tumor invasion.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2012;22(4):309-24. doi: 10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.v22.i4.50. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2012. PMID: 23272801 Review.
-
Interaction of tumour cells with their microenvironment: ion channels and cell adhesion molecules. A focus on pancreatic cancer.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014 Feb 3;369(1638):20130101. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0101. Print 2014 Mar 19. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24493749 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Local weakening of cell-extracellular matrix adhesion triggers basal epithelial tissue folding.EMBO J. 2025 Apr;44(7):2002-2024. doi: 10.1038/s44318-025-00384-6. Epub 2025 Feb 17. EMBO J. 2025. PMID: 39962267 Free PMC article.
-
Clonal effects of the Ras oncogene revealed by somatic mutagenesis in a Drosophila cancer model.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 10:2025.05.08.652841. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.08.652841. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40654754 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- White D.E., Kurpios N.A., Zuo D., Hassell J.A., Blaess S., Mueller U., Muller W.J. Targeted disruption of beta1-integrin in a transgenic mouse model of human breast cancer reveals an essential role in mammary tumor induction. Cancer Cell. 2004;6:159–170. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2004.06.025. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

