Isoquercitrin from Apocynum venetum L. Exerts Antiaging Effects on Yeasts via Stress Resistance Improvement and Mitophagy Induction through the Sch9/Rim15/Msn Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 38001792
- PMCID: PMC10669743
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12111939
Isoquercitrin from Apocynum venetum L. Exerts Antiaging Effects on Yeasts via Stress Resistance Improvement and Mitophagy Induction through the Sch9/Rim15/Msn Signaling Pathway
Abstract
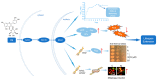
Background: With the development of an aging sociality, aging-related diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes, are dramatically increasing. To find small molecules from natural products that can prevent the aging of human beings and the occurrence of these diseases, we used the lifespan assay of yeast as a bioassay system to screen an antiaging substance. Isoquercitrin (IQ), an antiaging substance, was isolated from Apocynum venetum L., an herbal tea commonly consumed in Xinjiang, China.
Aim of the study: In the present study, we utilized molecular-biology technology to clarify the mechanism of action of IQ.
Methods: The replicative lifespans of K6001 yeasts and the chronological lifespans of YOM36 yeasts were used to screen and confirm the antiaging effect of IQ. Furthermore, the reactive oxygen species (ROS) and malondialdehyde (MDA) assay, the survival assay of yeast under stresses, real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and Western blotting analyses, the replicative-lifespan assay of mutants, such as Δsod1, Δsod2, Δgpx, Δcat, Δskn7, Δuth1, Δatg32, Δatg2, and Δrim15 of K6001, autophagy flux analysis, and a lifespan assay of K6001 yeast after giving a mitophagy inhibitor and activator were performed.
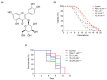
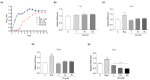
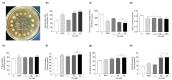
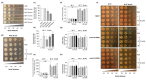
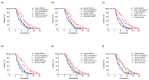
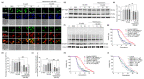
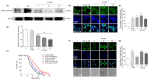
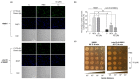
Results: IQ extended the replicative lifespans of the K6001 yeasts and the chronological lifespans of the YOM36 yeasts. Furthermore, the reactive nitrogen species (RNS) showed no change during the growth phase but significantly decreased in the stationary phase after treatment with IQ. The survival rates of the yeasts under oxidative- and thermal-stress conditions improved upon IQ treatment, and thermal stress was alleviated by the increasing superoxide dismutase (Sod) activity. Additionally, IQ decreased the ROS and MDA of the yeast while increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes. However, it could not prolong the replicative lifespans of Δsod1, Δsod2, Δgpx, Δcat, Δskn7, and Δuth1 of K6001. IQ significantly increased autophagy and mitophagy induction, the presence of free green fluorescent protein (GFP) in the cytoplasm, and ubiquitination in the mitochondria of the YOM38 yeasts at the protein level. IQ did not prolong the replicative lifespans of Δatg2 and Δatg32 of K6001. Moreover, IQ treatment led to a decrease in Sch9 at the protein level and an increase in the nuclear translocation of Rim15 and Msn2.
Conclusions: These results indicated that the Sch9/Rim15/Msn signaling pathway, as well as antioxidative stress, anti-thermal stress, and autophagy, were involved in the antiaging effects of IQ in the yeasts.
Keywords: Sch9/Rim15/Msn; anti-thermal stress; antiaging; antioxidative stress; isoquercitrin; mitophagy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Involvement of the Sch9/Rim15/Msn2 signaling pathway in the anti-aging activity of dendrobine from Dendrobium nobile Lindl. via modification of oxidative stress and autophagy.Chin Med. 2023 Sep 5;18(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s13020-023-00827-4. Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 37670345 Free PMC article.
-
Inokosterone from Gentiana rigescens Franch Extends the Longevity of Yeast and Mammalian Cells via Antioxidative Stress and Mitophagy Induction.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jan 23;11(2):214. doi: 10.3390/antiox11020214. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35204097 Free PMC article.
-
β-Cyclocitral from Lavandula angustifolia Mill. Exerts Anti-Aging Effects on Yeasts and Mammalian Cells via Telomere Protection, Antioxidative Stress, and Autophagy Activation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jun 12;13(6):715. doi: 10.3390/antiox13060715. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929154 Free PMC article.
-
Starvation signals in yeast are integrated to coordinate metabolic reprogramming and stress response to ensure longevity.Curr Genet. 2017 Oct;63(5):839-843. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0697-4. Epub 2017 Apr 25. Curr Genet. 2017. PMID: 28444510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiaging effects of bioactive molecules isolated from plants and fungi.Med Res Rev. 2019 Sep;39(5):1515-1552. doi: 10.1002/med.21559. Epub 2019 Jan 15. Med Res Rev. 2019. PMID: 30648267 Review.
Cited by
-
An Integrated Network Pharmacology and RNA-seq Approach for Exploring the Protective Effect of Isoquercitrin in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity: Identification of Novel Genes.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2025 Apr;25(4):541-558. doi: 10.1007/s12012-025-09968-4. Epub 2025 Feb 18. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39964600
References
-
- Dogra S., Dunstan D.W., Sugiyama T., Stathi A., Gardiner P.A., Owen N. Active aging and public health: Evidence, implications, and opportunities. Annu. Rev. Public Health. 2022;43:439–459. - PubMed
-
- Farooqui T., Farooqui A.A. Aging: An important factor for the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2009;130:203–215. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

