Oxidation of Arabidopsis thaliana COX19 Using the Combined Action of ERV1 and Glutathione
- PMID: 38001802
- PMCID: PMC10669224
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12111949
Oxidation of Arabidopsis thaliana COX19 Using the Combined Action of ERV1 and Glutathione
Abstract
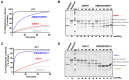
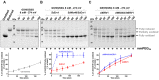
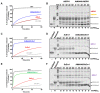
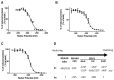
Protein import and oxidative folding within the intermembrane space (IMS) of mitochondria relies on the MIA40-ERV1 couple. The MIA40 oxidoreductase usually performs substrate recognition and oxidation and is then regenerated by the FAD-dependent oxidase ERV1. In most eukaryotes, both proteins are essential; however, MIA40 is dispensable in Arabidopsis thaliana. Previous complementation experiments have studied yeast mia40 mutants expressing a redox inactive, but import-competent versions of yeast Mia40 using A. thaliana ERV1 (AtERV1) suggest that AtERV1 catalyzes the oxidation of MIA40 substrates. We assessed the ability of both yeast and Arabidopsis MIA40 and ERV1 recombinant proteins to oxidize the apo-cytochrome reductase CCMH and the cytochrome c oxidase assembly protein COX19, a typical MIA40 substrate, in the presence or absence of glutathione, using in vitro cysteine alkylation and cytochrome c reduction assays. The presence of glutathione used at a physiological concentration and redox potential was sufficient to support the oxidation of COX19 by AtERV1, providing a likely explanation for why MIA40 is not essential for the import and oxidative folding of IMS-located proteins in Arabidopsis. The results point to fundamental biochemical differences between Arabidopsis and yeast ERV1 in catalyzing protein oxidation.
Keywords: ERV1; MIA40; glutathione; mitochondrial intermembrane space; oxidative folding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Erv1 of Arabidopsis thaliana can directly oxidize mitochondrial intermembrane space proteins in the absence of redox-active Mia40.BMC Biol. 2017 Nov 8;15(1):106. doi: 10.1186/s12915-017-0445-8. BMC Biol. 2017. PMID: 29117860 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic characterisation of Erv1, a key component for protein import and folding in yeast mitochondria.FEBS J. 2020 Mar;287(6):1220-1231. doi: 10.1111/febs.15077. Epub 2019 Oct 16. FEBS J. 2020. PMID: 31569302 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenesis of yeast Mia40 - uncoupling folding from import and atypical recognition features.FEBS J. 2013 Oct;280(20):4960-9. doi: 10.1111/febs.12482. Epub 2013 Sep 2. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 23937629
-
The Erv1-Mia40 disulfide relay system in the intermembrane space of mitochondria.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Apr;1783(4):601-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2007.12.005. Epub 2007 Dec 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18179776 Review.
-
The mitochondrial intermembrane space: a hub for oxidative folding linked to protein biogenesis.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013 Jul 1;19(1):54-62. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4855. Epub 2012 Oct 3. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013. PMID: 22901034 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

