Tocotrienols Provide Radioprotection to Multiple Organ Systems through Complementary Mechanisms of Antioxidant and Signaling Effects
- PMID: 38001840
- PMCID: PMC10668991
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12111987
Tocotrienols Provide Radioprotection to Multiple Organ Systems through Complementary Mechanisms of Antioxidant and Signaling Effects
Abstract
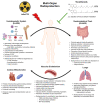
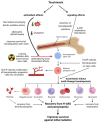
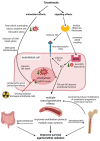
Tocotrienols have powerful radioprotective properties in multiple organ systems and are promising candidates for development as clinically effective radiation countermeasures. To facilitate their development as clinical radiation countermeasures, it is crucial to understand the mechanisms behind their powerful multi-organ radioprotective properties. In this context, their antioxidant effects are recognized for directly preventing oxidative damage to cellular biomolecules from ionizing radiation. However, there is a growing body of evidence indicating that the radioprotective mechanism of action for tocotrienols extends beyond their antioxidant properties. This raises a new pharmacological paradigm that tocotrienols are uniquely efficacious radioprotectors due to a synergistic combination of antioxidant and other signaling effects. In this review, we have covered the wide range of multi-organ radioprotective effects observed for tocotrienols and the mechanisms underlying it. These radioprotective effects for tocotrienols can be characterized as (1) direct cytoprotective effects, characteristic of the classic antioxidant properties, and (2) other effects that modulate a wide array of critical signaling factors involved in radiation injury.
Keywords: antioxidant; delta-tocotrienol; gamma-tocotrienol; mechanism of action; radiation countermeasures; radiation injury; radioprotection; signaling effects; tocotrienols.
Conflict of interest statement
The University of Arkansas and Tocol Pharmaceuticals, LLC have applied for patent protection on tocoflexols and other tocotrienol-containing products. A potential royalty stream to Nukhet Aykin-Burns, Philip J. Breen, Cesar M. Compadre, Darin E. Jones, Shraddha Thakkar, and Edith Nathalie Pineda may occur, consistent with the University of Arkansas policy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vitamin E: tocopherols and tocotrienols as potential radiation countermeasures.J Radiat Res. 2013 Nov 1;54(6):973-88. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrt048. Epub 2013 May 8. J Radiat Res. 2013. PMID: 23658414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidant Tocols as Radiation Countermeasures (Challenges to be Addressed to Use Tocols as Radiation Countermeasures in Humans).Antioxidants (Basel). 2018 Feb 23;7(2):33. doi: 10.3390/antiox7020033. Antioxidants (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29473853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Indian Indigenous Fruits as Radioprotective Agents: Past, Present and Future.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022;22(1):53-63. doi: 10.2174/1871520621666210706124315. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 34229590 Review.
-
Vitamin E Analogs as Radiation Response Modifiers.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:741301. doi: 10.1155/2015/741301. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 26366184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential suppression of proliferation in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells exposed to alpha-, gamma- and delta-tocotrienols is accompanied by altered expression of oxidative stress modulatory enzymes.Anticancer Res. 2010 Oct;30(10):4169-76. Anticancer Res. 2010. PMID: 21036737
Cited by
-
The use of vitamin E in ocular health: Bridging omics approaches with Tocopherol and Tocotrienol in the management of glaucoma.Food Chem (Oxf). 2024 Sep 24;9:100224. doi: 10.1016/j.fochms.2024.100224. eCollection 2024 Dec 30. Food Chem (Oxf). 2024. PMID: 39415777 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Radiation and Nuclear Countermeasures Program Strategic Plan and Research Agenda for Medical Countermeasures against Radiological and Nuclear Threats Progress Report: 2005–2011 and Future Directions: 2012–2016. [(accessed on 22 March 2022)]; Available online: https://www.niaid.nih.gov/sites/default/files/radnucprogressreport.pdf.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

