Multistep Approach Points to Compounds Responsible for the Biological Activity and Safety of Hydrolates from Nine Lamiaceae Medicinal Plants on Human Skin Fibroblasts
- PMID: 38001841
- PMCID: PMC10669667
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox12111988
Multistep Approach Points to Compounds Responsible for the Biological Activity and Safety of Hydrolates from Nine Lamiaceae Medicinal Plants on Human Skin Fibroblasts
Abstract
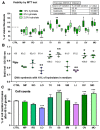
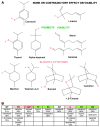
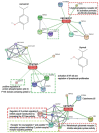
As byproducts of essential oil distillation, hydrolates are used in natural cosmetics/biomedicine due to their beneficial skin effects. However, data on their safety with relevant biological targets, such as human skin cells, are scarce. Therefore, we have tested nine hydrolates from the Lamiaceae family with skin fibroblasts that are responsible for extracellular collagenous matrix builds. Thyme, oregano, and winter savoury hydrolates showed several times higher total phenolics, which correlated strongly with their radical scavenging and antioxidative capacity; there was no correlation between their viability profiles and the reducing sugar levels. No proteins/peptides were detected. All hydrolates appeared safe for prolonged skin exposure except for 10-fold diluted lavender, which showed cytotoxicity (~20%), as well as rosemary and lavandin (~10%) using viability, DNA synthesis, and cell count testing. Clary sage, oregano, lemon balm, and thyme hydrolates (10-fold diluted) increased fibroblast viability and/or proliferation by 10-30% compared with the control, while their viability remained unaffected by Mentha and winter savoury. In line with the STITCH database, increased viability could be attributed to thymol presence in oregano and thyme hydrolates in lemon balm, which is most likely attributable to neral and geranial. The proliferative effect of clary sage could be supported by alpha-terpineol, not linalool. The major volatile organic compounds (VOCs) associated with cytotoxic effects on fibroblasts were borneol, 1,8-cineole, and terpinene-4-ol. Further research with pure compounds is warranted to confirm the roles of VOCs in the observed effects that are relevant to cosmetic and wound healing aspects.
Keywords: STITCH database; anti-proliferative effects; hydrolates; natural cosmetics; proliferative effects; skin fibroblast viability; volatile organic compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chemical Composition of Natural Hydrolates and Their Antimicrobial Activity on Arcobacter-Like Cells in Comparison with Other Microorganisms.Molecules. 2020 Nov 30;25(23):5654. doi: 10.3390/molecules25235654. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33266263 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Candida and Antibiofilm Activity of Selected Lamiaceae Essential Oils.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 Feb 16;28(2):28. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2802028. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023. PMID: 36866556
-
Thymus mastichina (L.) L. and Cistus ladanifer L. for skin application: chemical characterization and in vitro bioactivity assessment.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Feb 10;302(Pt A):115830. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115830. Epub 2022 Oct 13. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36243295
-
Potential of selected Lamiaceae plants in anti(retro)viral therapy.Pharmacol Res. 2018 Jul;133:301-314. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.12.016. Epub 2017 Dec 16. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 29258916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant essential oils and allied volatile fractions as multifunctional additives in meat and fish-based food products: a review.Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 2015;32(7):1049-64. doi: 10.1080/19440049.2015.1040081. Epub 2015 May 8. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 2015. PMID: 25893282 Review.
Cited by
-
Optimization of Flavonoid Extraction from Abelmoschus manihot Flowers Using Ultrasonic Techniques: Predictive Modeling through Response Surface Methodology and Deep Neural Network and Biological Activity Assessment.Molecules. 2024 Jun 1;29(11):2610. doi: 10.3390/molecules29112610. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38893486 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the Potential of Hydrosols: Transforming Essential Oil Byproducts into Valuable Resources.Molecules. 2024 Sep 30;29(19):4660. doi: 10.3390/molecules29194660. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39407589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Cinnamomum burmannii Essential Oil in Promoting Wound Healing.Molecules. 2024 Apr 30;29(9):2080. doi: 10.3390/molecules29092080. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38731569 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Helichrysum italicum in Promoting Collagen Deposition and Skin Regeneration in a New Dynamic Model of Skin Wound Healing.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 26;25(9):4736. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094736. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38731954 Free PMC article.
-
Green Extraction of Bioactives from Curcuma longa Using Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents: Unlocking Antioxidative, Antimicrobial, Antidiabetic, and Skin Depigmentation Potentials.Plants (Basel). 2025 Jan 8;14(2):163. doi: 10.3390/plants14020163. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39861517 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thiab S., Mhaidat N.M., Taha M.A., Thiab S., Koraysh S., Abutayeh R., Basheti I. A systematic review of randomized controlled trials assessing phytochemicals and natural ingredients for skin and hair care. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2021;11:20–45. doi: 10.7324/JAPS.2021.110703. - DOI
-
- Aly N., Benoit E., Chaubard J.-L., Chintalapudi K., Choung S., de Leeuw M., Diaz M., Dueppen D., Ferraro B., Fischetti V., et al. Cosmetic Potential of a Recombinant 50 kDa Protein. Cosmetics. 2022;9:8. doi: 10.3390/cosmetics9010008. - DOI
-
- Bhadauriya P., Jadon A., Upadhyay C. Study on use, attitude and knowledge of herbal cosmetic products among consumers: Health management. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2021;4:1–3. doi: 10.31069/japsr.v4i2.1. - DOI
-
- Sarkic A., Stappen I. Essential Oils and Their Single Compounds in Cosmetics—A Critical Review. Cosmetics. 2018;5:11. doi: 10.3390/cosmetics5010011. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

