Circulating Total Extracellular Vesicles Cargo Are Associated with Age-Related Oxidative Stress and Susceptibility to Cardiovascular Diseases: Exploratory Results from Microarray Data
- PMID: 38001921
- PMCID: PMC10669226
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11112920
Circulating Total Extracellular Vesicles Cargo Are Associated with Age-Related Oxidative Stress and Susceptibility to Cardiovascular Diseases: Exploratory Results from Microarray Data
Abstract
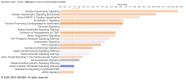
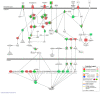
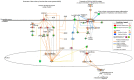
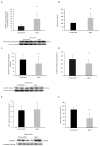
Aging is a risk factor for many non-communicable diseases such as cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. Extracellular vesicles and particles (EVP) carry microRNAs that may play a role in age-related diseases and may induce oxidative stress. We hypothesized that aging could impact EVP miRNA and impair redox homeostasis, contributing to chronic age-related diseases. Our aims were to investigate the microRNA profiles of circulating total EVPs from aged and young adult animals and to evaluate the pro- and antioxidant machinery in circulating total EVPs. Plasma from 3- and 21-month-old male Wistar rats were collected, and total EVPs were isolated. MicroRNA isolation and microarray expression analysis were performed on EVPs to determine the predicted regulation of targeted mRNAs. Thirty-one mature microRNAs in circulating EVPs were impacted by age and were predicted to target molecules in canonical pathways directly related to cardiovascular diseases and oxidative status. Circulating total EVPs from aged rats had significantly higher NADPH oxidase levels and myeloperoxidase activity, whereas catalase activity was significantly reduced in EVPs from aged animals. Our data shows that circulating total EVP cargo-specifically microRNAs and oxidative enzymes-are involved in redox imbalance in the aging process and can potentially drive cardiovascular aging and, consequently, cardiac disease.
Keywords: NADPH oxidase; aging; cardiac aging; extracellular vesicles and particles; redox homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Circulating Extracellular Vesicles and Particles Derived From Adipocytes: The Potential Role in Spreading MicroRNAs Associated With Cellular Senescence.Front Aging. 2022 Aug 9;3:867100. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2022.867100. eCollection 2022. Front Aging. 2022. PMID: 36016863 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of exercise modalities on BDNF and IL-1β content in circulating total extracellular vesicles and particles obtained from aged rats.Exp Gerontol. 2020 Dec;142:111124. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2020.111124. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Exp Gerontol. 2020. PMID: 33148515
-
Potential involvement of circulating extracellular vesicles and particles on exercise effects in malignancies.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 3;14:1121390. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1121390. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36936170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiRNAs that target amyloid precursor protein processing machinery in extracellular vesicles and particles derived from oral squamous cells carcinoma.J Oral Pathol Med. 2023 Oct;52(9):877-884. doi: 10.1111/jop.13475. Epub 2023 Aug 7. J Oral Pathol Med. 2023. PMID: 37549991
-
The human neurosecretome: extracellular vesicles and particles (EVPs) of the brain for intercellular communication, therapy, and liquid-biopsy applications.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 May 17;10:1156821. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1156821. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37266331 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Editorial for Special Issue "Cellular Senescence: Recent Cellular Advances and Discoveries".Biomedicines. 2024 Dec 9;12(12):2796. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12122796. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39767702 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding the role of extracellular vesicles in pathogenesis of cystic fibrosis.Mol Cell Pediatr. 2025 Apr 21;12(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s40348-025-00190-4. Mol Cell Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40257719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles and Therapeutic Targeting of Exosomes in Sepsis-Induced Cardiomyopathy.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Apr;29(8):e70559. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70559. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40264381 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bertoldi K., Cechinel L.R., Schallenberger B., Corssac G.B., Davies S., Guerreiro I.C.K., Belló-Klein A., Araujo A.S.R., Siqueira I.R. Circulating Extracellular Vesicles in the Aging Process: Impact of Aerobic Exercise. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018;440:115–125. doi: 10.1007/s11010-017-3160-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gomes de Andrade G., Reck Cechinel L., Bertoldi K., Galvão F., Valdeci Worm P., Rodrigues Siqueira I. The Aging Process Alters IL-1β and CD63 Levels Differently in Extracellular Vesicles Obtained from the Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2018;25:18–22. doi: 10.1159/000488943. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Davies S.M., Poljak A., Duncan M.W., Smythe G.A., Murphy M.P. Measurements of Protein Carbonyls, Ortho- and Meta-Tyrosine and Oxidative Phosphorylation Complex Activity in Mitochondria from Young and Old Rats. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001;31:181–190. doi: 10.1016/S0891-5849(01)00576-7. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

