Role of Akt/Protein Kinase B in Cancer Metastasis
- PMID: 38002001
- PMCID: PMC10669635
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11113001
Role of Akt/Protein Kinase B in Cancer Metastasis
Abstract
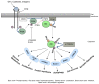
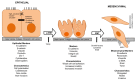
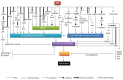
Metastasis is a critical step in the process of carcinogenesis and a vast majority of cancer-related mortalities result from metastatic disease that is resistant to current therapies. Cell migration and invasion are the first steps of the metastasis process, which mainly occurs by two important biological mechanisms, i.e., cytoskeletal remodelling and epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT). Akt (also known as protein kinase B) is a central signalling molecule of the PI3K-Akt signalling pathway. Aberrant activation of this pathway has been identified in a wide range of cancers. Several studies have revealed that Akt actively engages with the migratory process in motile cells, including metastatic cancer cells. The downstream signalling mechanism of Akt in cell migration depends upon the tumour type, sites, and intracellular localisation of activated Akt. In this review, we focus on the role of Akt in the regulation of two events that control cell migration and invasion in various cancers including head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) and the status of PI3K-Akt pathway inhibitors in clinical trials in metastatic cancers.
Keywords: Akt; EMT; HNSCC; cancer; cytoskeletal remodelling; metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bicarbonate transporter SLC4A7 promotes EMT and metastasis of HNSCC by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Mol Carcinog. 2023 May;62(5):628-640. doi: 10.1002/mc.23511. Epub 2023 Feb 2. Mol Carcinog. 2023. PMID: 36727616
-
FERMT1 knockdown inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition by inactivating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.BMC Oral Health. 2021 Nov 23;21(1):598. doi: 10.1186/s12903-021-01955-9. BMC Oral Health. 2021. PMID: 34814915 Free PMC article.
-
p70S6K promotes IL-6-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 14;7(24):36539-36550. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9282. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27174914 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway as a Radiosensitization in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 12;23(24):15749. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415749. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PI3K/AKT signaling pathway as a critical regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal tumor cells.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Aug 14;21(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01225-x. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37580737 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular pathways and targeted therapies in head and neck cancers pathogenesis.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 17;14:1373821. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1373821. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38952548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Akt-phosphorylated UFL1 UFMylates ArpC4 to promote metastasis.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2025 Aug;32(8):1528-1541. doi: 10.1038/s41594-025-01576-8. Epub 2025 May 26. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40419786
-
In vivo investigation of PEDV transmission via nasal infection: mechanisms of CD4+ T-cell-mediated intestinal infection.J Virol. 2025 Apr 15;99(4):e0176124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01761-24. Epub 2025 Mar 17. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40094365 Free PMC article.
-
A dynamic co-expression approach reveals Gins2 as a potential upstream modulator of HNSCC metastasis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 27;15(1):3322. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82668-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39865116 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leber M.F., Efferth T. Molecular principles of cancer invasion and metastasis (review) Int. J. Oncol. 2009;34:881–895. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

