Antiproliferative Effects in Colorectal Cancer and Stabilisation in Cyclodextrins of the Phytoalexin Isorhapontigenin
- PMID: 38002023
- PMCID: PMC10669587
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11113023
Antiproliferative Effects in Colorectal Cancer and Stabilisation in Cyclodextrins of the Phytoalexin Isorhapontigenin
Abstract
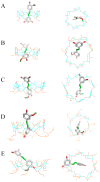
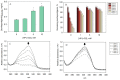
Isorhapontigenin has been proposed as a better alternative for oral administration than the famous resveratrol, as it shares many biological activities, but with a structure that could make its delivery easier. Although this hydrophobic structure could enhance bioavailability, it could also be a disadvantage in the development of products. In this research, we study the antiproliferative activity of this stilbene against colorectal cancer and overcome its limitations through molecular encapsulation in cyclodextrins. The cytotoxic activity against human colorectal cancer cells of isorhapontigenin was similar to that of resveratrol or piceatannol, supporting its use as a bioactive alternative. The study of the encapsulation through fluorescence spectroscopy and molecular docking revealed that the complexation satisfies a 1:1 stoichiometry and that HP-β-CD is the most suitable CD to encapsulate this stilbene. Through a spectrophotometric assay, it was observed that this CD could double the basal water solubility, exceeding the solubility of other hydroxylated stilbenes. The stability of these inclusion complexes was higher at a pH below 9 and refrigeration temperatures. Moreover, the use of CDs retained more than 78% of isorhapontigenin after storage for 12 weeks, compared to 15% in free form. Overall, these findings could help design novel formulations to better deliver isorhapontigenin.
Keywords: cancer; encapsulation; isorhapontigenin; solubility; stability; stilbene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Improvement of the Physicochemical Limitations of Rhapontigenin, a Cytotoxic Analogue of Resveratrol against Colon Cancer.Biomolecules. 2023 Aug 20;13(8):1270. doi: 10.3390/biom13081270. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37627335 Free PMC article.
-
Encapsulation of piceatannol, a naturally occurring hydroxylated analogue of resveratrol, by natural and modified cyclodextrins.Food Funct. 2016 May 18;7(5):2367-73. doi: 10.1039/c6fo00557h. Epub 2016 May 4. Food Funct. 2016. PMID: 27142512
-
Molecular encapsulation and bioactivity of gnetol, a resveratrol analogue, for use in foods.J Sci Food Agric. 2022 Aug 15;102(10):4296-4303. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.11781. Epub 2022 Feb 2. J Sci Food Agric. 2022. PMID: 35043401 Free PMC article.
-
Isorhapontigenin: exploring a promising resveratrol analog for disease management through diverse signaling pathways-a review with computational insights.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 17. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04176-x. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40244453 Review.
-
Cyclodextrins.Toxicol Pathol. 2008 Jan;36(1):30-42. doi: 10.1177/0192623307310945. Toxicol Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18337219 Review.
Cited by
-
Isocorydine Exerts Anticancer Activity by Disrupting the Energy Metabolism and Filamentous Actin Structures of Oral Squamous Carcinoma Cells.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jan 9;46(1):650-662. doi: 10.3390/cimb46010042. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38248344 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling Isorhapontigenin's therapeutic potential in lung cancer via integrated network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental validation.Sci Rep. 2025 May 29;15(1):18784. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01648-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40442126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Navarro-Orcajada S., Conesa I., Vidal-Sánchez F.J., Matencio A., Albaladejo-Maricó L., García-Carmona F., López-Nicolás J.M. Stilbenes: Characterization, Bioactivity, Encapsulation and Structural Modifications. A Review of Their Current Limitations and Promising Approaches. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022;63:7269–7287. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2045558. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- PID2021-122896NB-I00 (MCI/AEI/10.13039/501100011033/FEDER, UE)/Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación
- 21269/FPI/19/Fundación Séneca - Agencia de Ciencia y Tecnología de la Región de Murcia
- FPU-UM/University of Murcia
- FPU21/03503/Ministerio de Universidades
- 1062/2021/Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

