Transient Expression in HEK-293 Cells in Suspension Culture as a Rapid and Powerful Tool: SARS-CoV-2 N and Chimeric SARS-CoV-2N-CD154 Proteins as a Case Study
- PMID: 38002050
- PMCID: PMC10669214
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11113050
Transient Expression in HEK-293 Cells in Suspension Culture as a Rapid and Powerful Tool: SARS-CoV-2 N and Chimeric SARS-CoV-2N-CD154 Proteins as a Case Study
Abstract
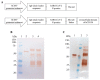
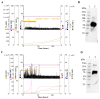
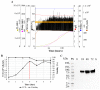
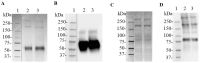
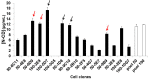
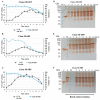
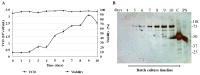
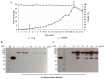
In a previous work, we proposed a vaccine chimeric antigen based on the fusion of the SARS-CoV-2 N protein to the extracellular domain of the human CD40 ligand (CD154). This vaccine antigen was named N-CD protein and its expression was carried out in HEK-293 stably transfected cells, grown in adherent conditions and serum-supplemented medium. The chimeric protein obtained in these conditions presented a consistent pattern of degradation. The immunization of mice and monkeys with this chimeric protein was able to induce a high N-specific IgG response with only two doses in pre-clinical experiments. In order to explore ways to diminish protein degradation, in the present work, the N and N-CD proteins were produced in suspension cultures and serum-free media following transient transfection of the HEK-293 clone 3F6, at different scales, including stirred-tank controlled bioreactors. The results showed negligible or no degradation of the target proteins. Further, clones stably expressing N-CD were obtained and adapted to suspension culture, obtaining similar results to those observed in the transient expression experiments in HEK-293-3F6. The evidence supports transient protein expression in suspension cultures and serum-free media as a powerful tool to produce in a short period of time high levels of complex proteins susceptible to degradation, such as the SARS-CoV-2 N protein.
Keywords: HEK-293; N protein; SARS-CoV-2; serum-free; suspension culture; transient expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Production and characterization of a chimeric antigen, based on nucleocapsid of SARS-CoV-2 fused to the extracellular domain of human CD154 in HEK-293 cells as a vaccine candidate against COVID-19.PLoS One. 2023 Sep 26;18(9):e0288006. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288006. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37751460 Free PMC article.
-
Chimeric Antigen by the Fusion of SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain with the Extracellular Domain of Human CD154: A Promising Improved Vaccine Candidate.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Jun 3;10(6):897. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10060897. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35746505 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid procedure to generate stably transfected HEK293 suspension cells for recombinant protein manufacturing: Yield improvements, bioreactor production and downstream processing.Protein Expr Purif. 2023 Oct;210:106295. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2023.106295. Epub 2023 May 16. Protein Expr Purif. 2023. PMID: 37201590
-
Plasticity of the HEK-293 cells, related to the culture media, as platform to produce a subunit vaccine against classical swine fever virus.AMB Express. 2019 Sep 5;9(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s13568-019-0864-8. AMB Express. 2019. PMID: 31486941 Free PMC article.
-
Transition from serum-supplemented monolayer to serum-free suspension lentiviral vector production for generation of chimeric antigen receptor T cells.Cytotherapy. 2022 Aug;24(8):850-860. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2022.03.014. Epub 2022 May 25. Cytotherapy. 2022. PMID: 35643755
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

