The Analysis of Selected miRNAs and Target MDM2 Gene Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 38002053
- PMCID: PMC10668942
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11113053
The Analysis of Selected miRNAs and Target MDM2 Gene Expression in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
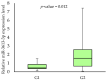
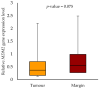
MiRNAs could play an important role in tumorigenesis and progression. The oncoprotein MDM2 (murine double minute 2) was identified as a negative regulator of the tumour suppressor p53. This study aims to analyse the expression of the MDM2 target miRNA candidates (miR-3613-3p, miR-371b-5p and miR-3658) and the MDM2 gene in oral squamous cell carcinoma tumour and margin samples and their association with the selected socio-demographic and clinicopathological characteristics. The study group consisted of 50 patients. The miRNAs and MDM2 gene expression levels were assessed by qPCR. The expression analysis of the miRNAs showed the expression of only one of them, i.e., miR-3613-3p. We found no statistically significant differences in the miR-3613-3p expression in tumour samples compared to the margin samples. When analysing the effect of smoking on miR-3613-3p expression, we demonstrated a statistically significant difference between smokers and non-smokers. In addition, we showed an association between the miR-3613-3p expression level and some clinical parameters in tumour samples (T, N and G). Our study demonstrates that miR-3613-3p overexpression is involved in the tumour progression of OSCC. This indicates that miR-3613-3p possesses potential prognostic values.
Keywords: MDM2; OSCC; margin; miR-3613-3p; miR-3658; miR-371b-5p; oral squamous cell carcinoma; tumour.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




Similar articles
-
miR-125b-5p, miR-155-3p, and miR-214-5p and Target E2F2 Gene in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 28;24(7):6320. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076320. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047293 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Expression of miR-486-3p, miR-548-3p, miR-561-5p and miR-509-5p in Tumor Biopsies of Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Pathogens. 2022 Feb 5;11(2):211. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11020211. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35215154 Free PMC article.
-
Study of MicroRNA (miR-221-3p, miR-133a-3p, and miR-9-5p) Expressions in Oral Submucous Fibrosis and Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Indian J Clin Biochem. 2023 Jan;38(1):73-82. doi: 10.1007/s12291-022-01035-x. Epub 2022 Apr 29. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36684498 Free PMC article.
-
Oral squamous cell carcinoma: microRNA expression profiling and integrative analyses for elucidation of tumourigenesis mechanism.Mol Cancer. 2016 Apr 7;15:28. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0512-8. Mol Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27056547 Free PMC article.
-
miR-877-3p as a Potential Tumour Suppressor of Oesophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Anticancer Res. 2023 Jan;43(1):35-43. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.16131. Anticancer Res. 2023. PMID: 36585184
References
-
- Golusinski P., Di Maio P., Pehlivan B., Colley S., Nankivell P., Kong A., Hartley A., Mehanna H. Evidence for the approach to the diagnostic evaluation of squamous cell carcinoma occult primary tumors of the head and neck. Oral Oncol. 2019;88:145–152. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2018.11.020. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aghiorghiesei O., Zanoaga O., Raduly L., Aghiorghiesei A.I., Chiroi P., Trif A., Buiga R., Budisan L., Lucaciu O., Pop L.A., et al. Dysregulation of miR-21-5p, miR-93-5p, miR-200c-3p and miR-205-5p in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Potential Biomarkers Panel? Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022;44:1754–1767. doi: 10.3390/cimb44040121. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dioguardi M., Caloro G.A., Laino L., Alovisi M., Sovereto D., Crincoli V., Aiuto R., Coccia E., Troiano G., Lo Muzio L. Circulating miR-21 as a Potential Biomarker for the Diagnosis of Oral Cancer: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2020;12:936. doi: 10.3390/cancers12040936. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

