Pharmacogenetic Association between Allelic Variants of the Autophagy-Related Genes and Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Treatment Response in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration
- PMID: 38002079
- PMCID: PMC10669692
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines11113079
Pharmacogenetic Association between Allelic Variants of the Autophagy-Related Genes and Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Treatment Response in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Abstract
Background: Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the leading cause of late-onset blindness in elderly. The occurrence and development of AMD is a multifactorial complex process where autophagy plays an important role. The first-line drugs for neovascular AMD (nAMD) are inhibitors of VEGF, with up to 30% of patients having an incomplete response to treatment. Genetic factors may influence the response to anti-VEGF therapy and explain treatment outcome variability. We aimed to estimate the role of polymorphic markers of the MTOR (rs1064261, rs1057079, rs11121704, rs2295080), SQSTM1 (rs10277), ULK1 (rs11246867, rs3088051), MAP1LC3A (rs73105013) and ATG5 (rs573775) genes in the development of nAMD and the efficacy of anti-VEGF therapy response.
Methods: Genotyping by allele-specific PCR was performed in 317 controls and 315 nAMD patients in the Russian population. Of them, 196 treatment-naive nAMD patients underwent three monthly intravitreal injections (IVIs) of aflibercept. Genotypic frequencies were compared with OCT markers of therapy effectiveness and best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) measures. The main outcomes were the BCVA gain and decrease in central retinal thickness (CRT).
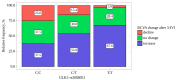
Results: MTOR-rs1057079-C, MTOR-rs11121704-C and MTOR-rs2295080-G alleles were associated with an increased risk of nAMD. The BCVA was increased in 117 (59.7%) patients by 10 [5-20] letters, did not changed in 59 (30.1%), and was decreased in 20 (10.2%) patients. ULK1-rs3088051 was associated with BCVA change. Among patients with the TT and CT genotypes for ULK1-rs3088051, an improvement in visual acuity was noted in 67.6% and 53.8% of cases, while in patients with the CC genotype, an increase in BCVA was recorded in 37.5% of cases (p = 0.01). The decrease in CRT was associated with SQSTM1-rs10277 (p = 0.001): it was significantly higher in TT (93 [58-122] mkm) and CT (66 [30-105] mkm) carriers compared to the CC genotype (47 [24-68] mkm). Other SNPs did not show significant associations with the outcome of anti-VEGF treatment.
Conclusions: MTOR gene polymorphisms are moderately associated with the risk of nAMD. SQSTM1-rs10277 and ULK1-rs3088051 may influence short-term response to intravitreal anti-VEGF treatment. The results suggest that autophagy could be a target for future drugs to overcome resistance to anti-VEGF therapy.
Keywords: aflibercept; age-related macular degeneration; autophagy; pharmacogenetics; response to anti-VEGF therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Autophagy Genes for Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration in a Finnish Case-Control Study.Genes (Basel). 2020 Nov 6;11(11):1318. doi: 10.3390/genes11111318. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33172148 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between Aflibercept Efficacy and Genetic Variants of Genes Associated with Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration: The BIOIMAGE Trial.Ophthalmologica. 2020;243(6):461-470. doi: 10.1159/000508902. Epub 2020 May 26. Ophthalmologica. 2020. PMID: 32454495
-
Analysis of the association between CFH Y402H polymorphism and response to intravitreal ranibizumab in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD).Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2018 Aug 1;18(3):260-267. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2018.2493. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 29579408 Free PMC article.
-
Real-World Effectiveness and Real-World Cost-Effectiveness of Intravitreal Aflibercept and Intravitreal Ranibizumab in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Real-World Studies.Adv Ther. 2020 Jan;37(1):300-315. doi: 10.1007/s12325-019-01147-6. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Adv Ther. 2020. PMID: 31728825 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of High-Dose Intravitreal Aflibercept in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration (nAMD): A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2025 Jan 24;17(1):e77906. doi: 10.7759/cureus.77906. eCollection 2025 Jan. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 39991354 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advanced Research in Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Special Issue.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 8;12(2):392. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020392. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38397993 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fursova A.Z., Derbeneva A.S., Vasilyeva M.A., Nikulich I.F., Tarasov M.S., Gamza Y.A., Chubar N.V., Gusarevitch O.G., Dmitrieva E.I., Kozhevnikova O.S., et al. New findings on pathogenetic mechanisms in the development of age-related macular degeneration. Vestn. Oftalmol. 2022;138:120–130. doi: 10.17116/oftalma2022138021120. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Spaide R.F., Jaffe G.J., Sarraf D., Freund K.B., Sadda S.R., Staurenghi G., Waheed N.K., Chakravarthy U., Rosenfeld P.J., Holz F.G., et al. Consensus Nomenclature for Reporting Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration Data: Consensus on Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration Nomenclature Study Group. Ophthalmology. 2020;127:616–636. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2019.11.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous