Natural Polyketides Act as Promising Antifungal Agents
- PMID: 38002254
- PMCID: PMC10669366
- DOI: 10.3390/biom13111572
Natural Polyketides Act as Promising Antifungal Agents
Abstract
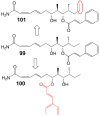
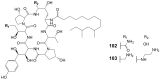
Invasive fungal infections present a significant risk to human health. The current arsenal of antifungal drugs is hindered by drug resistance, limited antifungal range, inadequate safety profiles, and low oral bioavailability. Consequently, there is an urgent imperative to develop novel antifungal medications for clinical application. This comprehensive review provides a summary of the antifungal properties and mechanisms exhibited by natural polyketides, encompassing macrolide polyethers, polyether polyketides, xanthone polyketides, linear polyketides, hybrid polyketide non-ribosomal peptides, and pyridine derivatives. Investigating natural polyketide compounds and their derivatives has demonstrated their remarkable efficacy and promising clinical application as antifungal agents.
Keywords: antifungal; invasive fungal infections; polyketides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

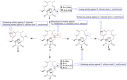
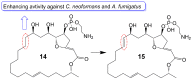
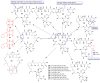

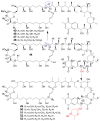
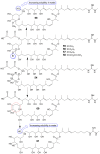



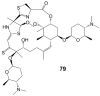
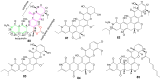
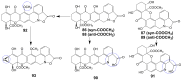



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

