8-Hydroxydaidzein Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits AML-Associated Gene Expression in U-937 Cells: Potential Phytochemical for AML Treatment
- PMID: 38002257
- PMCID: PMC10669020
- DOI: 10.3390/biom13111575
8-Hydroxydaidzein Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits AML-Associated Gene Expression in U-937 Cells: Potential Phytochemical for AML Treatment
Abstract
Background: 8-hydroxydaidzein (8-OHD) is a compound derived from daidzein, known for its anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative properties in K562 human chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cells. However, its effects on acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells have not been fully understood.
Method: To investigate its potential anti-AML mechanism, we employed an integrated in vitro-in silico approach.
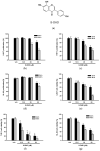
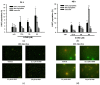
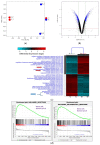
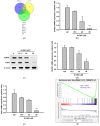
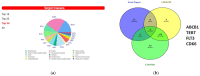
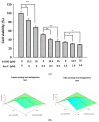
Results: Our findings demonstrate that 8-OHD suppresses the expression of CDK6 and CCND2 proteins and induces cell apoptosis in U-937 cells by activating Caspase-7 and cleaving PARP-1. Microarray analysis revealed that 8-OHD downregulates differentially expressed genes (DEGs) associated with rRNA processing and ribosome biogenesis pathways. Moreover, AML-target genes, including CCND2, MYC, NPM1, FLT3, and TERT, were downregulated by 8-OHD. Additionally, molecular docking software predicted that 8-OHD has the potential to interact with CDK6, FLT3, and TERT proteins, thereby reducing their activity and inhibiting cell proliferation. Notably, we discovered a synergic pharmacological interaction between 8-OHD and cytarabine (Ara-C).
Conclusions: Overall, this study provides insights into the therapeutic applications of 8-OHD in treating AML and elucidates its underlying mechanisms of action.
Keywords: 8-hydroxydaidzein; CDK6; acute myeloid leukemia; apoptosis; caspase-7.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
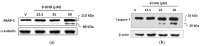







Similar articles
-
8-Hydroxydaidzein, an Isoflavone from Fermented Soybean, Induces Autophagy, Apoptosis, Differentiation, and Degradation of Oncoprotein BCR-ABL in K562 Cells.Biomedicines. 2020 Nov 16;8(11):506. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8110506. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 33207739 Free PMC article.
-
8-Hydroxydaidzein Downregulates JAK/STAT, MMP, Oxidative Phosphorylation, and PI3K/AKT Pathways in K562 Cells.Biomedicines. 2021 Dec 14;9(12):1907. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9121907. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34944720 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-155 as an inducer of apoptosis and cell differentiation in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia.Mol Cancer. 2014 Apr 5;13:79. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-79. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24708856 Free PMC article.
-
Radotinib enhances cytarabine (Ara-C)-induced acute myeloid leukemia cell death.BMC Cancer. 2020 Dec 4;20(1):1193. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07701-8. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33276759 Free PMC article.
-
When the good go bad: Mutant NPM1 in acute myeloid leukemia.Blood Rev. 2018 May;32(3):167-183. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2017.11.001. Epub 2017 Nov 4. Blood Rev. 2018. PMID: 29157973 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Biochanin A in AML Cells: Apoptosis Induction and Pathway-Specific Regulation in U937 and THP-1.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 31;26(11):5317. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115317. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40508126 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review of phytochemical approaches in treatment of acute myeloid leukemia: Associated pathways and molecular mechanisms.Chin Herb Med. 2024 Nov 26;17(1):41-55. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2024.11.010. eCollection 2025 Jan. Chin Herb Med. 2024. PMID: 39949810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelet-derived microparticles enhance Ara-C-induced cell death in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Nalm-6).Bioimpacts. 2024 Oct 29;15:30454. doi: 10.34172/bi.30454. eCollection 2025. Bioimpacts. 2024. PMID: 40256222 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

