Efficacy of Sub-Gingivally Delivered Propolis Nanoparticle in Non-Surgical Management of Periodontal Pocket: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 38002260
- PMCID: PMC10669236
- DOI: 10.3390/biom13111576
Efficacy of Sub-Gingivally Delivered Propolis Nanoparticle in Non-Surgical Management of Periodontal Pocket: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
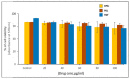
Naturally sourced products like propolis are commonly employed for the non-surgical treatment of periodontal pockets. The use of nanoparticle formulations of these natural remedies has the potential to improve treatment outcomes. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the efficacy of sub-gingivally delivered propolis nanoparticles in the non-surgical management of periodontal pockets. Forty patients diagnosed with periodontitis presenting at least one periodontal pocket with a probing pocket depth between 4 and 6 mm were selected. Patients were randomly assigned into the control group (n = 20), which received scaling and root planing (SRP) and saline (SRP + Saline), and the test group (n = 20), which received SRP and sub-gingivally delivered propolis nanoparticles (PRO) into the periodontal pocket (SRP + PRO). The clinical parameters recorded were plaque index (PI), gingival index (GI), relative attachment loss (RAL), probing pocket depth (PPD), and bleeding on probing (BOP). They were assessed at baseline, one month, and three months post therapy. The results indicated that there was a significant improvement in clinical parameters (p < 0.05) in the test sites compared with the control sites at the end of the study. The gingival index at one month and three months was found to be significantly better in the SRP + PRO group than the SRP + Saline group, with a p value of <0.001. The BOP, PPD, and RAL showed significant improvement with the SRP + PRO group at the end of the 3-month follow-up with p values of 0.0001, 0.001, and 0.05, respectively. The subgingival delivery of propolis nanoparticles showed promising results as an adjunct to SRP in patients with periodontitis presenting periodontal pockets.
Keywords: chronic periodontitis; local drug delivery; periodontal pocket; propolis nanoparticle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Utilisation of locally delivered doxycycline in non-surgical treatment of chronic periodontitis. A comparative multi-centre trial of 2 treatment approaches.J Clin Periodontol. 2001 Aug;28(8):753-61. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-051x.2001.280806.x. J Clin Periodontol. 2001. PMID: 11442735 Clinical Trial. English, French, German.
-
Clinical evaluation of the combined efficacy of injectable platelet-rich fibrin along with scaling and root planing in the non-surgical periodontal therapy of stage III and grade C periodontitis patients having type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial.Clin Adv Periodontics. 2024 Sep;14(3):223-231. doi: 10.1002/cap.10266. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Clin Adv Periodontics. 2024. PMID: 37749861 Clinical Trial.
-
Quadrant root planing versus same-day full-mouth root planing. I. Clinical findings.J Clin Periodontol. 2004 Feb;31(2):132-40. doi: 10.1111/j.0303-6979.2004.00461.x. J Clin Periodontol. 2004. PMID: 15016039 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical effect of azithromycin as an adjunct to non-surgical treatment of chronic periodontitis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials.J Periodontal Res. 2016 Jun;51(3):275-83. doi: 10.1111/jre.12319. Epub 2015 Sep 12. J Periodontal Res. 2016. PMID: 26362529 Review.
-
The benefits of propolis in periodontal therapy. A scoping review of preclinical and clinical studies.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Mar 1;303:115926. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115926. Epub 2022 Nov 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36400346
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial Properties of Hive Products and Their Potential Applications in Human and Veterinary Medicine.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Feb 10;14(2):172. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14020172. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40001416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical and microbiological effects of a propolis toothpaste in patients with periodontitis under supportive periodontal therapy: a randomized double-blind clinical trial.Clin Oral Investig. 2025 Jul 9;29(8):379. doi: 10.1007/s00784-025-06456-5. Clin Oral Investig. 2025. PMID: 40632341 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Effect of Topically Applied Melatonin and Vitamin C in the Non-surgical Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis: A Triple-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial.Cureus. 2024 Dec 31;16(12):e76676. doi: 10.7759/cureus.76676. eCollection 2024 Dec. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39886720 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges in Optimizing Nanoplatforms Used for Local and Systemic Delivery in the Oral Cavity.Pharmaceutics. 2024 May 7;16(5):626. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16050626. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38794288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative evaluation of propolis mouthwash with 0.2% chlorhexidine mouthwash as an adjunct to mechanical therapy in improving the periodontitis among perimenopausal women: a randomized controlled trial.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Jan 5;24(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03768-4. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38183081 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Lisbona-González M.J., Muñoz-Soto E., Reyes-Botella C., Olmedo-Gaya M.V., Diaz-Castro J., Moreno-Fernandez J. Study of the Antimicrobial Effect of an Ethanolic Extract of Propolis in Periodontal Disease. Appl. Sci. 2021;11:7463. doi: 10.3390/app11167463. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

