Currently Used Methods to Evaluate the Efficacy of Therapeutic Drugs and Kidney Safety
- PMID: 38002263
- PMCID: PMC10669823
- DOI: 10.3390/biom13111581
Currently Used Methods to Evaluate the Efficacy of Therapeutic Drugs and Kidney Safety
Abstract
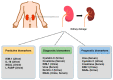
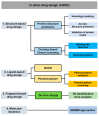
Kidney diseases with kidney failure or damage, such as chronic kidney disease (CKD) and acute kidney injury (AKI), are common clinical problems worldwide and have rapidly increased in prevalence, affecting millions of people in recent decades. A series of novel diagnostic or predictive biomarkers have been discovered over the past decade, enhancing the investigation of renal dysfunction in preclinical studies and clinical risk assessment for humans. Since multiple causes lead to renal failure, animal studies have been extensively used to identify specific disease biomarkers for understanding the potential targets and nephropathy events in therapeutic insights into disease progression. Mice are the most commonly used model to investigate the mechanism of human nephropathy, and the current alternative methods, including in vitro and in silico models, can offer quicker, cheaper, and more effective methods to avoid or reduce the unethical procedures of animal usage. This review provides modern approaches, including animal and nonanimal assays, that can be applied to study chronic nonclinical safety. These specific situations could be utilized in nonclinical or clinical drug development to provide information on kidney disease.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; alternative methods; biomarkers; chronic kidney disease; kidney disease models.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Review of Specific Biomarkers of Chronic Renal Injury and Their Potential Application in Nonclinical Safety Assessment Studies.Toxicol Pathol. 2021 Jul;49(5):996-1023. doi: 10.1177/0192623320985045. Epub 2021 Feb 12. Toxicol Pathol. 2021. PMID: 33576319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kidney disease models: tools to identify mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets.Zool Res. 2018 Mar 18;39(2):72-86. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2017.055. Zool Res. 2018. PMID: 29515089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers of renal function, which and when?Clin Chim Acta. 2015 Jan 1;438:350-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2014.08.039. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Clin Chim Acta. 2015. PMID: 25195004 Review.
-
AKI: an increasingly recognized risk factor for CKD development and progression.J Nephrol. 2020 Dec;33(6):1171-1187. doi: 10.1007/s40620-020-00793-2. Epub 2020 Jul 10. J Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32651850 Review.
-
Recombinant α-Klotho may be prophylactic and therapeutic for acute to chronic kidney disease progression and uremic cardiomyopathy.Kidney Int. 2017 May;91(5):1104-1114. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.10.034. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Kidney Int. 2017. PMID: 28131398 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of Waterpipe Smoke Exposure on Experimentally Induced Chronic Kidney Disease in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 2;25(1):585. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010585. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38203756 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Biomarkers for Chronic Kidney Disease in Older Individuals: Current Perspectives and Future Directions.Cureus. 2024 Sep 26;16(9):e70262. doi: 10.7759/cureus.70262. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39463626 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zabka T.S., Burkhardt J., Reagan W.J., Gautier J.-C., Glaab W.E., Guffroy M., Harding J., Brees D., McDuffie E., Ramaiah L., et al. The use of emerging safety biomarkers in nonclinical and clinical safety assessment—The current and future state: An IQ DruSafe industry survey. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021;120:104857. doi: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2020.104857. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Friedman L.S., Ostermeyer E.A., Lynch E.D., Szabo C.I., Anderson L.A., Dowd P., Lee M.K., Rowell S.E., Boyd J., King M.C. The search for BRCA1. Cancer Res. 1994;54:6374–6382. - PubMed
-
- Provenzano M., Rotundo S., Chiodini P., Gagliardi I., Michael A., Angotti E., Borrelli S., Serra R., Foti D., De Sarro G., et al. Contribution of Predictive and Prognostic Biomarkers to Clinical Research on Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020;21:5846. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165846. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MOST 109-2314-B-038-078-MY3/The Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan
- MOST 110-2314-B-038-075-MY3/The Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan
- MOST 111-2314-B-038-154/The Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan
- NSTC 112-2314-B-038-087/The Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan
- NSTC 112-2221-E-038-016/The Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

