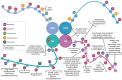
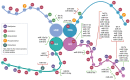
MicroRNA-Mediated Regulation of Histone-Modifying Enzymes in Cancer: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications
- PMID: 38002272
- PMCID: PMC10669115
- DOI: 10.3390/biom13111590
MicroRNA-Mediated Regulation of Histone-Modifying Enzymes in Cancer: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
In the past decade, significant advances in molecular research have provided a deeper understanding of the intricate regulatory mechanisms involved in carcinogenesis. MicroRNAs, short non-coding RNA sequences, exert substantial influence on gene expression by repressing translation or inducing mRNA degradation. In the context of cancer, miRNA dysregulation is prevalent and closely associated with various stages of carcinogenesis, including initiation, progression, and metastasis. One crucial aspect of the cancer phenotype is the activity of histone-modifying enzymes that govern chromatin accessibility for transcription factors, thus impacting gene expression. Recent studies have revealed that miRNAs play a significant role in modulating these histone-modifying enzymes, leading to significant implications for genes related to proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis in cancer cells. This article provides an overview of current research on the mechanisms by which miRNAs regulate the activity of histone-modifying enzymes in the context of cancer. Both direct and indirect mechanisms through which miRNAs influence enzyme expression are discussed. Additionally, potential therapeutic implications arising from miRNA manipulation to selectively impact histone-modifying enzyme activity are presented. The insights from this analysis hold significant therapeutic promise, suggesting the utility of miRNAs as tools for the precise regulation of chromatin-related processes and gene expression. A contemporary focus on molecular regulatory mechanisms opens therapeutic pathways that can effectively influence the control of tumor cell growth and dissemination.
Keywords: cancer; epigenetics; gene regulation; histone-modifying enzymes; microRNA; therapeutic implications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The crosstalk between miRNAs and signaling pathways in human cancers: Potential therapeutic implications.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2024;386:133-165. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2023.12.001. Epub 2024 Jan 23. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38782498 Review.
-
The Functions of Histone Modification Enzymes in Cancer.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2016;17(5):438-45. doi: 10.2174/1389203717666160122120521. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2016. PMID: 26796305 Review.
-
A step-by-step microRNA guide to cancer development and metastasis.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2017 Aug;40(4):303-339. doi: 10.1007/s13402-017-0341-9. Epub 2017 Jul 26. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2017. PMID: 28748501 Review.
-
MicroRNA-99 family in cancer: molecular mechanisms for clinical applications.PeerJ. 2025 Mar 27;13:e19188. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19188. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40161350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs and Epigenetics.Adv Cancer Res. 2017;135:189-220. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2017.06.003. Epub 2017 Aug 4. Adv Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28882223 Review.
Cited by
-
Unlocking the Potential of Circulating miRNAs as Biomarkers in Glioblastoma.Life (Basel). 2024 Oct 16;14(10):1312. doi: 10.3390/life14101312. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal microRNA as a key regulator of PI3K/AKT pathways in human tumors.Med Oncol. 2024 Oct 14;41(11):265. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02529-9. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39400677 Review.
-
Targeting epigenetic regulators as a promising avenue to overcome cancer therapy resistance.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Jul 18;10(1):219. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02266-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40675967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KLF4 is an epigenetically modulated, context-dependent tumor suppressor.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jul 29;12:1392391. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1392391. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39135777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Functions and Regulatory Mechanisms of Histone Modifications in Skeletal Muscle Development and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 12;26(8):3644. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083644. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332229 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous