The Growth-Inhibitory Effect of Increased Planting Density Can Be Reduced by Abscisic Acid-Degrading Bacteria
- PMID: 38002350
- PMCID: PMC10669761
- DOI: 10.3390/biom13111668
The Growth-Inhibitory Effect of Increased Planting Density Can Be Reduced by Abscisic Acid-Degrading Bacteria
Abstract
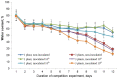
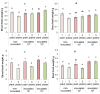
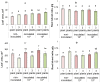
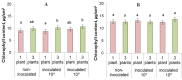
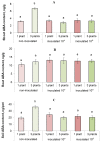
High-density planting can increase crop productivity per unit area of cultivated land. However, the application of this technology is limited by the inhibition of plant growth in the presence of neighbors, which is not only due to their competition for resources but is also caused by growth regulators. Specifically, the abscisic acid (ABA) accumulated in plants under increased density of planting has been shown to inhibit their growth. The goal of the present study was to test the hypothesis that bacteria capable of degrading ABA can reduce the growth inhibitory effect of competition among plants by reducing concentration of this hormone in plants and their environment. Lettuce plants were grown both individually and three per pot; the rhizosphere was inoculated with a strain of Pseudomonas plecoglossicida 2.4-D capable of degrading ABA. Plant growth was recorded in parallel with immunoassaying ABA concentration in the pots and plants. The presence of neighbors indeed inhibited the growth of non-inoculated lettuce plants. Bacterial inoculation positively affected the growth of grouped plants, reducing the negative effects of competition. The bacteria-induced increase in the mass of competing plants was greater than that in the single ones. ABA concentration was increased by the presence of neighbors both in soil and plant shoots associated with the inhibition of plant growth, but accumulation of this hormone as well as inhibition of the growth of grouped plants was prevented by bacteria. The results confirm the role of ABA in the response of plants to the presence of competitors as well as the possibility of reducing the negative effect of competition on plant productivity with the help of bacteria capable of degrading this hormone.
Keywords: Lactuca sativa L.; abscisic acid; growth; plant competition; plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR); planting density.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dependence of growth inhibiting action of increased planting density on capacity of lettuce plants to synthesize ABA.J Plant Physiol. 2018 Jan;220:69-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2017.09.011. Epub 2017 Nov 11. J Plant Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29149646
-
Abscisic acid metabolizing rhizobacteria decrease ABA concentrations in planta and alter plant growth.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2014 Jan;74:84-91. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.10.032. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24270514
-
Leaf Gas Exchange of Tomato Depends on Abscisic Acid and Jasmonic Acid in Response to Neighboring Plants under Different Soil Nitrogen Regimes.Plants (Basel). 2020 Nov 29;9(12):1674. doi: 10.3390/plants9121674. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33260470 Free PMC article.
-
Bacillus subtilis: A plant-growth promoting rhizobacterium that also impacts biotic stress.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2019 Sep;26(6):1291-1297. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2019.05.004. Epub 2019 May 20. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31516360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Persistence of Abscisic Acid Analogs in Plants: Chemical Control of Plant Growth and Physiology.Genes (Basel). 2023 May 13;14(5):1078. doi: 10.3390/genes14051078. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37239437 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria Bacillus subtilis IB-22 on the Hydraulic Conductivity and Abundance of PIP2 Aquaporins in the Roots of an Abscisic Acid-Deficient Barley Mutant.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 4;25(19):10706. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910706. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409034 Free PMC article.
-
Special Issue "Phytohormones 2022-2023".Biomolecules. 2024 Sep 11;14(9):1146. doi: 10.3390/biom14091146. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334912 Free PMC article.
-
Abscisic Acid Metabolizing Rhodococcus sp. Counteracts Phytopathogenic Effects of Abscisic Acid Producing Botrytis sp. on Sunflower Seedlings.Plants (Basel). 2025 Aug 7;14(15):2442. doi: 10.3390/plants14152442. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40805791 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Villalobos F., Fereres E. Principles of Agronomy for Sustainable Agriculture. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2016. p. 543. - DOI
-
- Fang X., Li Y., Nie J., Wang C., Huang K., Zhang K.Y., Zhang Y., She H., Xi L., Ruan R., et al. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer and planting density on the leaf photosynthetic characteristics, agronomic traits and grain yield in common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum M.) Field Crops Res. 2018;219:160–168. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2018.02.001. - DOI
-
- Jiang X., Tong L., Kang S., Li F., Li D., Qin Y., Shi R., Li J. Planting density affected biomass and grain yield of maize for seed production in an arid region of Northwest China. J. Arid Land. 2018;10:292–303. doi: 10.1007/s40333-018-0098-7. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

