Delivery of Growth Factors to Enhance Bone Repair
- PMID: 38002376
- PMCID: PMC10669014
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering10111252
Delivery of Growth Factors to Enhance Bone Repair
Abstract
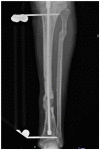
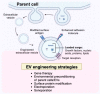
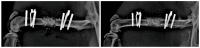
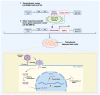
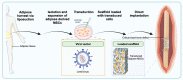
The management of critical-sized bone defects caused by nonunion, trauma, infection, malignancy, pseudoarthrosis, and osteolysis poses complex reconstruction challenges for orthopedic surgeons. Current treatment modalities, including autograft, allograft, and distraction osteogenesis, are insufficient for the diverse range of pathology encountered in clinical practice, with significant complications associated with each. Therefore, there is significant interest in the development of delivery vehicles for growth factors to aid in bone repair in these settings. This article reviews innovative strategies for the management of critical-sized bone loss, including novel scaffolds designed for controlled release of rhBMP, bioengineered extracellular vesicles for delivery of intracellular signaling molecules, and advances in regional gene therapy for sustained signaling strategies. Improvement in the delivery of growth factors to areas of significant bone loss has the potential to revolutionize current treatment for this complex clinical challenge.
Keywords: BMP; critical-sized defect; gene therapy; growth factor; stem cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

