Cerebellar Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Applied over Multiple Days Does Not Enhance Motor Learning of a Complex Overhand Throwing Task in Young Adults
- PMID: 38002389
- PMCID: PMC10669324
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering10111265
Cerebellar Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Applied over Multiple Days Does Not Enhance Motor Learning of a Complex Overhand Throwing Task in Young Adults
Abstract
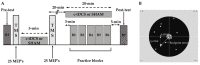
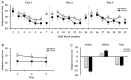
Cerebellar transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) enhances motor skill and learning in relatively simple motor tasks, but it is unclear if c-tDCS can improve motor performance in complex motor tasks. The purpose of this study was to determine the influence of c-tDCS applied over multiple days on motor learning in a complex overhand throwing task. In a double-blind, randomized, between-subjects, SHAM-controlled, experimental design, 30 young adults were assigned to either a c-tDCS or a SHAM group. Participants completed three identical experiments on consecutive days that involved overhand throwing in a pre-test block, five practice blocks with concurrent c-tDCS, and a post-test block. Overhand throwing endpoint accuracy was quantified as the endpoint error. The first dorsal interosseous muscle motor evoked potential (MEP) amplitude elicited by transcranial magnetic stimulation was used to quantify primary motor cortex (M1) excitability modulations via c-tDCS. Endpoint error significantly decreased over the 3 days of practice, but the magnitude of decrease was not significantly different between the c-tDCS and SHAM group. Similarly, MEP amplitude slightly increased from the pre-tests to the post-tests, but these increases did not differ between groups. These results indicate that multi-day c-tDCS does not improve motor learning in an overhand throwing task or increase M1 excitability.
Keywords: motor skill; transcranial direct current stimulation; transcranial magnetic stimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Motor Learning in a Complex Motor Task Is Unaffected by Three Consecutive Days of Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Jul 23;11(8):744. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11080744. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199702 Free PMC article.
-
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation of Primary Motor Cortex over Multiple Days Improves Motor Learning of a Complex Overhand Throwing Task.Brain Sci. 2023 Oct 10;13(10):1441. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13101441. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37891809 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebellar Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Enhances Motor Learning in a Complex Overhand Throwing Task.Cerebellum. 2019 Aug;18(4):813-816. doi: 10.1007/s12311-019-01040-6. Cerebellum. 2019. PMID: 31104285 Clinical Trial.
-
Long-Term Application of Cerebellar Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Does Not Improve Motor Learning in Parkinson's Disease.Cerebellum. 2022 Jun;21(3):333-349. doi: 10.1007/s12311-021-01297-w. Epub 2021 Jul 7. Cerebellum. 2022. PMID: 34232470 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Combined With Physical Training on the Excitability of the Motor Cortex, Physical Performance, and Motor Learning: A Systematic Review.Front Neurosci. 2021 Apr 9;15:648354. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.648354. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33897361 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Influence of Inter-Trial Interval on the Assessment of Short-Interval Intracortical Inhibition.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Jun 25;11(7):645. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11070645. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061727 Free PMC article.
-
Special Issue "Electric, Magnetic, and Electromagnetic Fields in Biology and Medicine: From Mechanisms to Biomedical Applications: 2nd Edition".Bioengineering (Basel). 2025 Jul 7;12(7):739. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering12070739. Bioengineering (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40722431 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Dominant Hemisphere Excitability Is Unaffected during and after Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation of the Dominant Hemisphere.Brain Sci. 2024 Jul 12;14(7):694. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14070694. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39061434 Free PMC article.
-
Motor Learning in a Complex Motor Task Is Unaffected by Three Consecutive Days of Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Jul 23;11(8):744. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11080744. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199702 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation on the Excitability of the Unstimulated Contralateral Primary Motor Cortex.Brain Sci. 2025 May 17;15(5):512. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15050512. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40426683 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buch E.R., Santarnecchi E., Antal A., Born J., Celnik P.A., Classen J., Gerloff C., Hallett M., Hummel F.C., Nitsche M.A., et al. Effects of tDCS on motor learning and memory formation: A consensus and critical position paper. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. J. Int. Fed. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017;128:589–603. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2017.01.004. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

