A Novel Registration Method for a Mixed Reality Navigation System Based on a Laser Crosshair Simulator: A Technical Note
- PMID: 38002414
- PMCID: PMC10669875
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering10111290
A Novel Registration Method for a Mixed Reality Navigation System Based on a Laser Crosshair Simulator: A Technical Note
Abstract
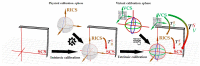
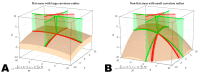
Mixed Reality Navigation (MRN) is pivotal in augmented reality-assisted intelligent neurosurgical interventions. However, existing MRN registration methods face challenges in concurrently achieving low user dependency, high accuracy, and clinical applicability. This study proposes and evaluates a novel registration method based on a laser crosshair simulator, evaluating its feasibility and accuracy. A novel registration method employing a laser crosshair simulator was introduced, designed to replicate the scanner frame's position on the patient. The system autonomously calculates the transformation, mapping coordinates from the tracking space to the reference image space. A mathematical model and workflow for registration were designed, and a Universal Windows Platform (UWP) application was developed on HoloLens-2. Finally, a head phantom was used to measure the system's target registration error (TRE). The proposed method was successfully implemented, obviating the need for user interactions with virtual objects during the registration process. Regarding accuracy, the average deviation was 3.7 ± 1.7 mm. This method shows encouraging results in efficiency and intuitiveness and marks a valuable advancement in low-cost, easy-to-use MRN systems. The potential for enhancing accuracy and adaptability in intervention procedures positions this approach as promising for improving surgical outcomes.
Keywords: accuracy; augmented reality; crosshair simulator; head phantom; laser; mixed reality navigation; neurosurgical interventions; preoperative planning; registration method; target registration error.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The Feasibility and Accuracy of Holographic Navigation with Laser Crosshair Simulator Registration on a Mixed-Reality Display.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jan 30;24(3):896. doi: 10.3390/s24030896. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339612 Free PMC article.
-
A new markerless patient-to-image registration method using a portable 3D scanner.Med Phys. 2014 Oct;41(10):101910. doi: 10.1118/1.4895847. Med Phys. 2014. PMID: 25281962
-
Holographic mixed-reality neuronavigation with a head-mounted device: technical feasibility and clinical application.Neurosurg Focus. 2021 Aug;51(2):E22. doi: 10.3171/2021.5.FOCUS21175. Neurosurg Focus. 2021. PMID: 34333462
-
Augmented Reality Surgical Navigation System for External Ventricular Drain.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Sep 21;10(10):1815. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10101815. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36292263 Free PMC article.
-
Image Overlay Surgery Based on Augmented Reality: A Systematic Review.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1260:175-195. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-47483-6_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 33211313
Cited by
-
Head model dataset for mixed reality navigation in neurosurgical interventions for intracranial lesions.Sci Data. 2024 May 25;11(1):538. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-03385-y. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 38796526 Free PMC article.
-
The Feasibility and Accuracy of Holographic Navigation with Laser Crosshair Simulator Registration on a Mixed-Reality Display.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jan 30;24(3):896. doi: 10.3390/s24030896. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339612 Free PMC article.
-
Extended Reality-Based Head-Mounted Displays for Surgical Education: A Ten-Year Systematic Review.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Jul 23;11(8):741. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11080741. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is Overlain Display a Right Choice for AR Navigation? A Qualitative Study of Head-Mounted Augmented Reality Surgical Navigation on Accuracy for Large-Scale Clinical Deployment.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025 Jan;31(1):e70217. doi: 10.1111/cns.70217. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2025. PMID: 39817491 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stieglitz L.H., Fichtner J., Andres R., Schucht P., Krähenbühl A.-K., Raabe A., Beck J. The silent loss of neuronavigation accuracy: A systematic retrospective analysis of factors influencing the mismatch of frameless stereotactic systems in cranial neurosurgery. Neurosurgery. 2013;72:796–807. doi: 10.1227/NEU.0b013e318287072d. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

