Mathematical and Machine Learning Models of Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Review
- PMID: 38002445
- PMCID: PMC10669004
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering10111320
Mathematical and Machine Learning Models of Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Review
Abstract
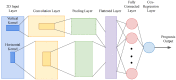
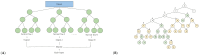
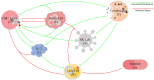
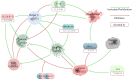
This review explores the multifaceted landscape of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) by delving into both mechanistic and machine learning models. While machine learning models leverage patients' gene expression and clinical data through a variety of techniques to predict patients' outcomes, mechanistic models focus on investigating cells' and molecules' interactions within RCC tumors. These interactions are notably centered around immune cells, cytokines, tumor cells, and the development of lung metastases. The insights gained from both machine learning and mechanistic models encompass critical aspects such as signature gene identification, sensitive interactions in the tumors' microenvironments, metastasis development in other organs, and the assessment of survival probabilities. By reviewing the models of RCC, this study aims to shed light on opportunities for the integration of machine learning and mechanistic modeling approaches for treatment optimization and the identification of specific targets, all of which are essential for enhancing patient outcomes.
Keywords: checkpoint inhibitors; differential equation; gene signature; machine learning; mathematical modeling; neural network; sunitinib.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- National Cancer Institute Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. [(accessed on 12 August 2020)]; Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/pediatric-adult-rare-tumor/rare-tumors/rare-kidne....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

