Neuromodulation Techniques in Children with Super-Refractory Status Epilepticus
- PMID: 38002487
- PMCID: PMC10670094
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci13111527
Neuromodulation Techniques in Children with Super-Refractory Status Epilepticus
Abstract
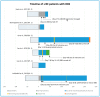
Status epilepticus (SE) is a life-threatening condition and medical emergency which can have lifelong consequences, including neuronal death and alteration of neuronal networks, resulting in long-term neurologic and cognitive deficits in children. When standard pharmacological treatment for SE is not successful in controlling seizures, the condition evolves to refractory SE (rSE) and finally to super-refractory SE (srSE) if it exceeds 24 h despite using anaesthetics. In this systematic review, we present literature data on the potential uses of clinical neuromodulation techniques for the management of srSE in children, including electroconvulsive therapy, vagus nerve stimulation, and deep brain stimulation. The evaluation of these techniques is limited by the small number of published paediatric cases (n = 25, one with two techniques) in peer-reviewed articles (n = 18). Although neuromodulation strategies have not been tested through randomised, prospective controlled clinical trials, this review presents the existing data and the potential benefits of neuromodulation therapy, suggesting that these techniques, when available, could be considered at earlier stages within the course of srSE intending to prevent long-term neurologic complications. Clinical trials aiming to establish whether early intervention can prevent long-term sequelae are necessary in order to establish the potential clinical value of neuromodulation techniques for the treatment of srSE in children.
Keywords: children epilepsy; deep brain stimulation; electroconvulsive therapy; neuromodulation; super-refractory status epilepticus; vagus nerve stimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
AV has received an honorarium for lectures and consultancy from Medtronic Ltd. The rest of the authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

