Implications of Social Anxiety Symptoms in Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Is There a Predictive Role of Interpersonal Sensitivity and Substance Abuse?
- PMID: 38002519
- PMCID: PMC10669824
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci13111559
Implications of Social Anxiety Symptoms in Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Is There a Predictive Role of Interpersonal Sensitivity and Substance Abuse?
Abstract
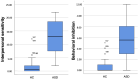
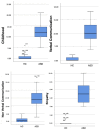
Social anxiety disorder (SAD) has been frequently reported by subjects with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). However, interestingly, the overlap between social anxiety and autistic traits may sometimes impede ASD diagnosis in subjects without intellectual or language impairment. The aim of the present work was to evaluate the presence and correlates of social phobic features among subjects with ASD, with a specific focus on evaluating which social anxiety symptoms may be statistically predictive of an ASD diagnosis. With this purpose, 48 subjects with ASD and 48 gender- and age- matched healthy controls (HCs) were recruited and assessed with the SHY-SV and the AdAS Spectrum questionnaires. Results highlighted higher scores in all SHY-SV Spectrum domains and total scores for the ASD group. Moreover, AdAS Spectrum scores were significantly correlated with all SHY-SV domain and total scores. A logistic regression analysis highlighted the SHY-SV Interpersonal sensitivity and Substance Abuse domains scores as significant positive predictors of an ASD diagnosis. These results confirm the link between ASD and SAD. Because of this association, particular attention should be paid to subjects with high interpersonal sensitivity traits and substance abuse problems.
Keywords: autism; autism spectrum disorder; interpersonal sensitivity; social anxiety disorder; substance abuse.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Presence and correlates of autistic traits among patients with social anxiety disorder.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Jan 19;14:1320558. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1320558. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38312918 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring the neglected anxiety disorder: validation of the social anxiety spectrum-short version (SHY-SV) questionnaire.BMC Psychiatry. 2023 Oct 2;23(1):708. doi: 10.1186/s12888-023-05137-5. BMC Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37784074 Free PMC article.
-
Panic-agoraphobic symptoms in adults with ASD: the role of ruminative thinking and inflexibility.CNS Spectr. 2024 May 9:1-7. doi: 10.1017/S1092852924000282. Online ahead of print. CNS Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38720482
-
Correlations Between the Development of Social Anxiety and Individuals With Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2023 Sep 7;15(9):e44841. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44841. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37809175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Sensory Abnormalities and Neuropsychopathology of Autism and Anxiety.Cureus. 2020 May 12;12(5):e8071. doi: 10.7759/cureus.8071. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 32542126 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Platelet Levels of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Is There a Specific Association with Autism Spectrum Psychopathology?Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 10;12(7):1529. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071529. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39062102 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC, USA: 2023.
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Autism: Recognition, Referral, Diagnosis and Management of Adults on the Autism Spectrum, NICE Guidelines [CG142] U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS); Washington, DC, USA: 2012.
-
- Simonoff E., Pickles A., Charman T., Chandler T., Baird G. Psychiatric disorders in children with autism spectrum disorders: Prevalence, comorbidity, and associated factors in a population-derived sample. J. Am. Acad. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry. 2008;47:921–929. doi: 10.1097/CHI.0b013e318179964f. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources