Personalized Neuromodulation: A Novel Strategy for Improving Tinnitus Treatment
- PMID: 38002601
- PMCID: PMC10672003
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12226987
Personalized Neuromodulation: A Novel Strategy for Improving Tinnitus Treatment
Abstract
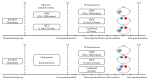
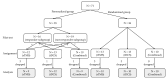
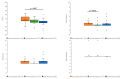
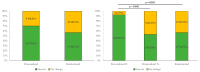
This study evaluated the efficacy of personalized neuromodulation, where treatment modalities are chosen based on the patient's responses in a pilot trial. A total of 71 patients with tinnitus were divided into two groups: a personalized group and a randomized neuromodulation group. In the personalized group (n = 35), repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) and transcranial direct-current stimulation (tDCS) were assessed in a pilot trial, and responsive modalities were administered to 16 patients, while the non-responders (n = 19) were randomly assigned to rTMS, tDCS, or combined modalities. Patients in the randomized group (n = 36) were randomly allocated to rTMS, tDCS, or combined modalities. The Tinnitus Handicap Inventory (THI) score improvement after 10 sessions of each neuromodulation was significantly greater in the personalized group than in the randomized group (p = 0.043), with no significant differences in tinnitus loudness, distress, or awareness. The treatment success rate was highest in the personalized responder subgroup (92.3%), and significantly greater than that in the non-responder subgroup (53.0%; p = 0.042) and the randomized group (56.7%; p = 0.033). Personalized neuromodulation, where the treatment modality is chosen based on the patient's responses in a pilot trial, is an advantageous strategy for treating tinnitus.
Keywords: neuromodulation; tinnitus; transcranial direct-current stimulation; transcranial magnetic stimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. This paper will be used as the doctoral dissertation of the first author, Seung Yeon Jeon.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison of Treatment Outcome between Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) and Transcutaneous Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS) in Intractable Tinnitus.J Clin Med. 2021 Feb 7;10(4):635. doi: 10.3390/jcm10040635. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33562396 Free PMC article.
-
Repeated Bilateral Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation over Auditory Cortex for Tinnitus Treatment: A Double-Blinded Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial.Brain Sci. 2024 Apr 12;14(4):373. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14040373. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38672022 Free PMC article.
-
Personalization of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for the Treatment of Chronic Subjective Tinnitus.Brain Sci. 2022 Jan 31;12(2):203. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12020203. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 35203965 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for the Treatment of Chronic Tinnitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Biomed Res Int. 2020 May 2;2020:3141278. doi: 10.1155/2020/3141278. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32461976 Free PMC article.
-
Non-invasive neuromodulation for tinnitus: A meta-analysis and modeling studies.Brain Stimul. 2021 Jan-Feb;14(1):113-128. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2020.11.014. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Brain Stimul. 2021. PMID: 33276156 Review.
Cited by
-
Anatomo-physiological basis and applied techniques of electrical neuromodulation in chronic pain.J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2024 May 2;4(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s44158-024-00167-1. J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2024. PMID: 38698460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between breast cancer risk factors and blood microbiome in patients with breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 19;15(1):6115. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-90180-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39972005 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the role of inflammatory cytokines in mediating the effect of gut microbiota on gastrointestinal cancers: a mendelian randomization study.Gastric Cancer. 2025 May;28(3):442-454. doi: 10.1007/s10120-025-01587-w. Epub 2025 Feb 17. Gastric Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39961989
References
-
- De Ridder D., Schlee W., Vanneste S., Londero A., Weisz N., Kleinjung T., Shekhawat G.S., Elgoyhen A.B., Song J.J., Andersson G., et al. Tinnitus and tinnitus disorder: Theoretical and operational definitions (an international multidisciplinary proposal) Prog. Brain Res. 2021;260:1–25. doi: 10.1016/bs.pbr.2020.12.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Simoes J.P., Daoud E., Shabbir M., Amanat S., Assouly K., Biswas R., Casolani C., Dode A., Enzler F., Jacquemin L., et al. Multidisciplinary Tinnitus Research: Challenges and Future Directions From the Perspective of Early Stage Researchers. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021;13:647285. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.647285. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

