Association of Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors with the Risk of Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Infection in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Nationwide Cohort Study
- PMID: 38002613
- PMCID: PMC10671978
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12226998
Association of Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors with the Risk of Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Infection in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Abstract
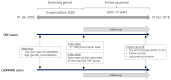
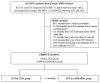
Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) are proposed as a risk factor for nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) infection. Limited research investigates NTM infection risk in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients treated with TNFi compared to conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs), considering other concurrent or prior non-TNFi antirheumatic drugs. We aimed to evaluate the NTM infection risk associated with TNFi using a real-world database. Patients with RA treated with TNFi or csDMARDs between 2005 and 2016 were identified utilizing the Korean National Health Insurance Service database. To minimize potential bias, we aligned the initiation year of csDMARDs for both TNFi and csDMARD users and tracked them from their respective treatment start dates. The association of TNFi with NTM infection risk was estimated in a one-to-one matched cohort using a multivariable conditional Cox regression analysis. In the matched cohort (n = 4556), the incidence rates of NTM infection were 2.47 and 3.66 per 1000 person-year in TNFi and csDMARD users. Compared to csDMARDs, TNFi did not increase the risk of NTM infection (adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) 0.517 (95% confidence interval, 0.205-1.301)). The TNFi use in RA patients was not associated with an increased risk of NTM infection compared to csDMARDs. Nevertheless, monitoring during TNFi treatment is crucial.
Keywords: cohort study; infection; nontuberculous mycobacteria; rheumatoid arthritis; tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TNF inhibitors increase the risk of nontuberculous mycobacteria in patients with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis in a mycobacterium tuberculosis endemic area.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 7;12(1):4003. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-07968-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35256729 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of malignancy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis after anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: results from Korean National Health Insurance claims data.Korean J Intern Med. 2019 May;34(3):669-677. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2016.374. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Korean J Intern Med. 2019. PMID: 29172405 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes Zoster Reactivation in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: Analysis of Disease Characteristics and Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2015 Dec;67(12):1671-8. doi: 10.1002/acr.22628. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2015. PMID: 26018115
-
Comparative Risk of Cardiovascular Events With Biologic and Synthetic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2020 Apr;72(4):561-576. doi: 10.1002/acr.23875. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2020. PMID: 30875456 Free PMC article.
-
Most Appropriate Conventional Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drug to Combine With Different Advanced Therapies in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Literature Review With Meta-Analysis.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2021 Jun;73(6):873-884. doi: 10.1002/acr.24195. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2021. PMID: 32216091
Cited by
-
The Inflammatory Link of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Thrombosis: Pathogenic Molecular Circuits and Treatment Approaches.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Apr 18;47(4):291. doi: 10.3390/cimb47040291. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40699690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CT informs detection and treatment options in rheumatoid arthritis complicated by pulmonary non-tuberculous mycobacterial disease from the FIRST registry.RMD Open. 2024 Jun 12;10(2):e004049. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-004049. RMD Open. 2024. PMID: 38866590 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonfiglioli K.R., de Medeiros Ribeiro A.C., Carnieletto A.P., Pereira I., Domiciano D.S., da Silva H.C., Pugliesi A., Pereira L.R., Guimaraes M.F.R., Giorgi R.D.N., et al. Extra-articular manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis remain a major challenge: Data from a large, multi-centric cohort. Adv. Rheumatol. 2023;63:34. doi: 10.1186/s42358-023-00318-y. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lin C.T., Huang W.N., Tsai W.C., Chen J.P., Hung W.T., Hsieh T.Y., Chen H.H., Hsieh C.W., Lai K.L., Tang K.T., et al. Predictors of drug survival for biologic and targeted synthetic DMARDs in rheumatoid arthritis: Analysis from the TRA Clinical Electronic Registry. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:e0250877. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250877. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

