Impact of the Body Composition on Knee Osteoarthritis Assessed Using Bioimpedance Analysis
- PMID: 38002651
- PMCID: PMC10672022
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12227037
Impact of the Body Composition on Knee Osteoarthritis Assessed Using Bioimpedance Analysis
Abstract
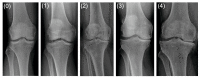
Osteoarthritis (OA) ranks among the most prevalent inflammatory diseases affecting the musculoskeletal system and is a leading cause of disability globally, impacting approximately 250 million individuals. This study aimed to assess the relationship between the severity of knee osteoarthritis (KOA) and body composition in postmenopausal women using bioimpedance analysis (BIA). The study included 58 postmenopausal females who were candidates for total knee arthroplasty. The control group consisted of 25 postmenopausal individuals with no degenerative knee joint changes. The anthropometric analysis encompassed the body mass index (BMI), mid-arm and mid-thigh circumferences (MAC and MTC), and triceps skinfold thickness (TSF). Functional performance was evaluated using the 30 s sit-to-stand test. During the BIA test, electrical parameters such as membrane potential, electrical resistance, capacitive reactance, impedance, and phase angle were measured. Additionally, body composition parameters, including Total Body Water (TBW), Extracellular Water (ECW), Intracellular Water (ICW), Body Cellular Mass (BCM), Extracellular Mass (ECM), Fat-Free Mass (FFM), and Fat Mass (FM), were examined. The study did not find any statistically significant differences in the electrical parameters between the control (0-1 grade on the K-L scale) and study groups (3-4 grade on the K-L scale). However, statistically significant differences were observed in BMI, fat mass (FM), arm circumference, triceps skinfold thickness, and sit-to-stand test results between the analyzed groups. In conclusion, the association between overweight and obesity with KOA in postmenopausal women appears to be primarily related to the level of adipose tissue and its metabolic activity.
Keywords: bioimpedance analysis; knee; osteoarthritis; postmenopausal females.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Body mass index and bioelectrical vector distribution in 8-year-old children.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2008 Feb;18(2):133-41. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2006.08.008. Epub 2007 Feb 16. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2008. PMID: 17307345
-
Dental agenesis and evaluation of body composition through bioelectrical impedance analysis. Observational study on a sample of paediatric subjects.Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2020 Jun;21(2):143-147. doi: 10.23804/ejpd.2020.21.02.09. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2020. PMID: 32567946
-
Does Isolated Unilateral Hip or Knee Osteoarthritis Lead to Adverse Changes in Extremity Composition?Iowa Orthop J. 2022 Jun;42(1):163-167. Iowa Orthop J. 2022. PMID: 35821924 Free PMC article.
-
[Body composition assessment before and after weight loss following a Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Are bioimpedanciometry estimations reliable?].Nutr Hosp. 2020 Dec 16;37(6):1150-1156. doi: 10.20960/nh.02942. Nutr Hosp. 2020. PMID: 33119392 Spanish.
-
Body fluid volumes measurements by impedance: A review of bioimpedance spectroscopy (BIS) and bioimpedance analysis (BIA) methods.Med Eng Phys. 2008 Dec;30(10):1257-69. doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2008.06.009. Epub 2008 Aug 3. Med Eng Phys. 2008. PMID: 18676172 Review.
Cited by
-
Nontraditional Factors Influencing Cardiovascular Disease Risk: Correlation Among Framingham Risk Score, Body Composition Index, and Sleep-Breathing Monitoring Index.Clin Transl Sci. 2025 Mar;18(3):e70170. doi: 10.1111/cts.70170. Clin Transl Sci. 2025. PMID: 40105259 Free PMC article.
-
Phase angle: a novel application of bioelectrical impedance technology in osteoarthritis screening and diagnosis.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 May;44(5):1877-1886. doi: 10.1007/s10067-025-07349-4. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40131594 Review.
References
-
- Jarecki J., Polkowska I., Kazimierczak W., Wójciak M., Sowa I., Dresler S., Blicharski T. Assessment of the Impact of Physical Activity on the Musculoskeletal System in Early Degenerative Knee Joint Lesions in an Animal Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023;24:3540. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043540. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

